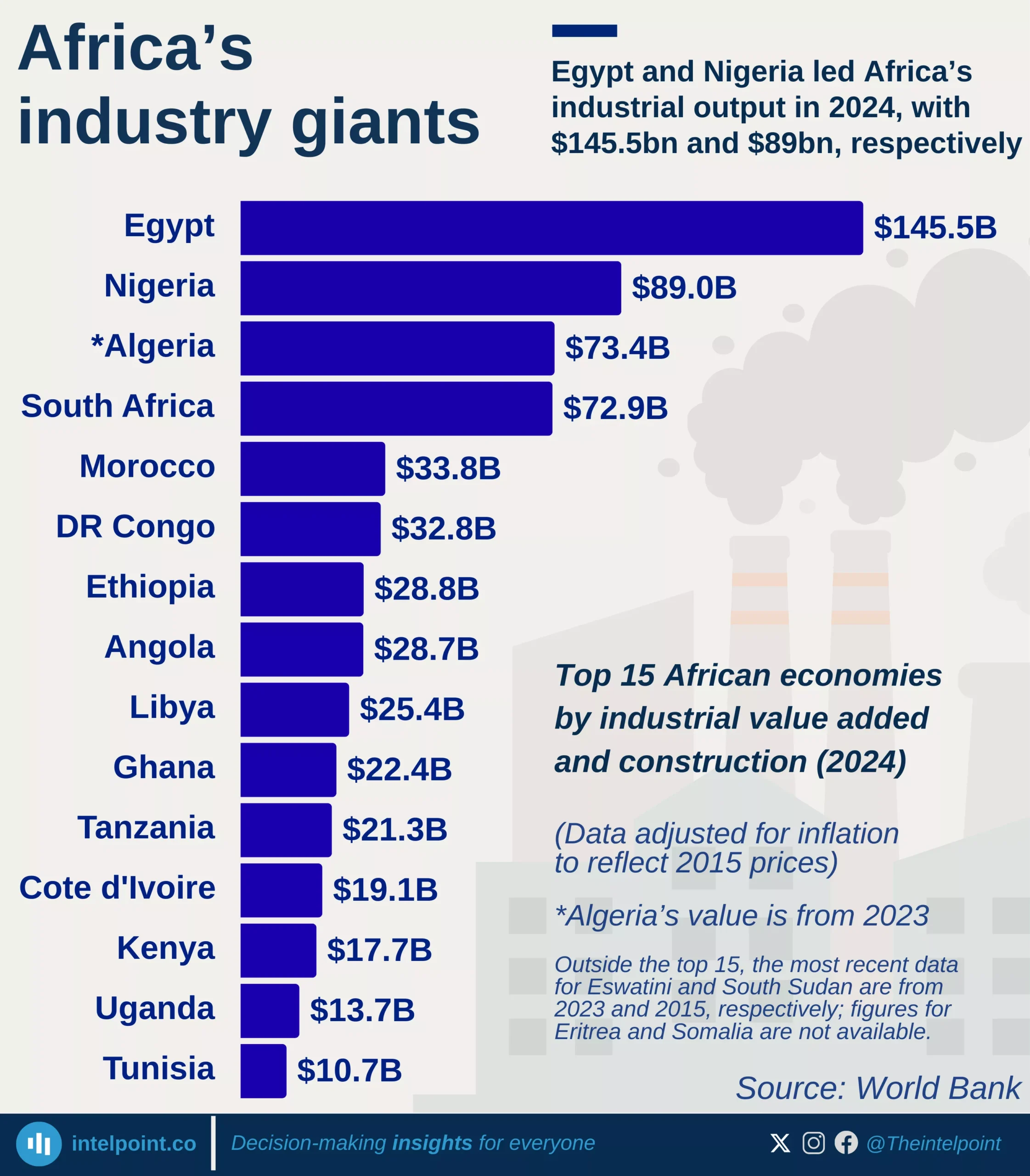
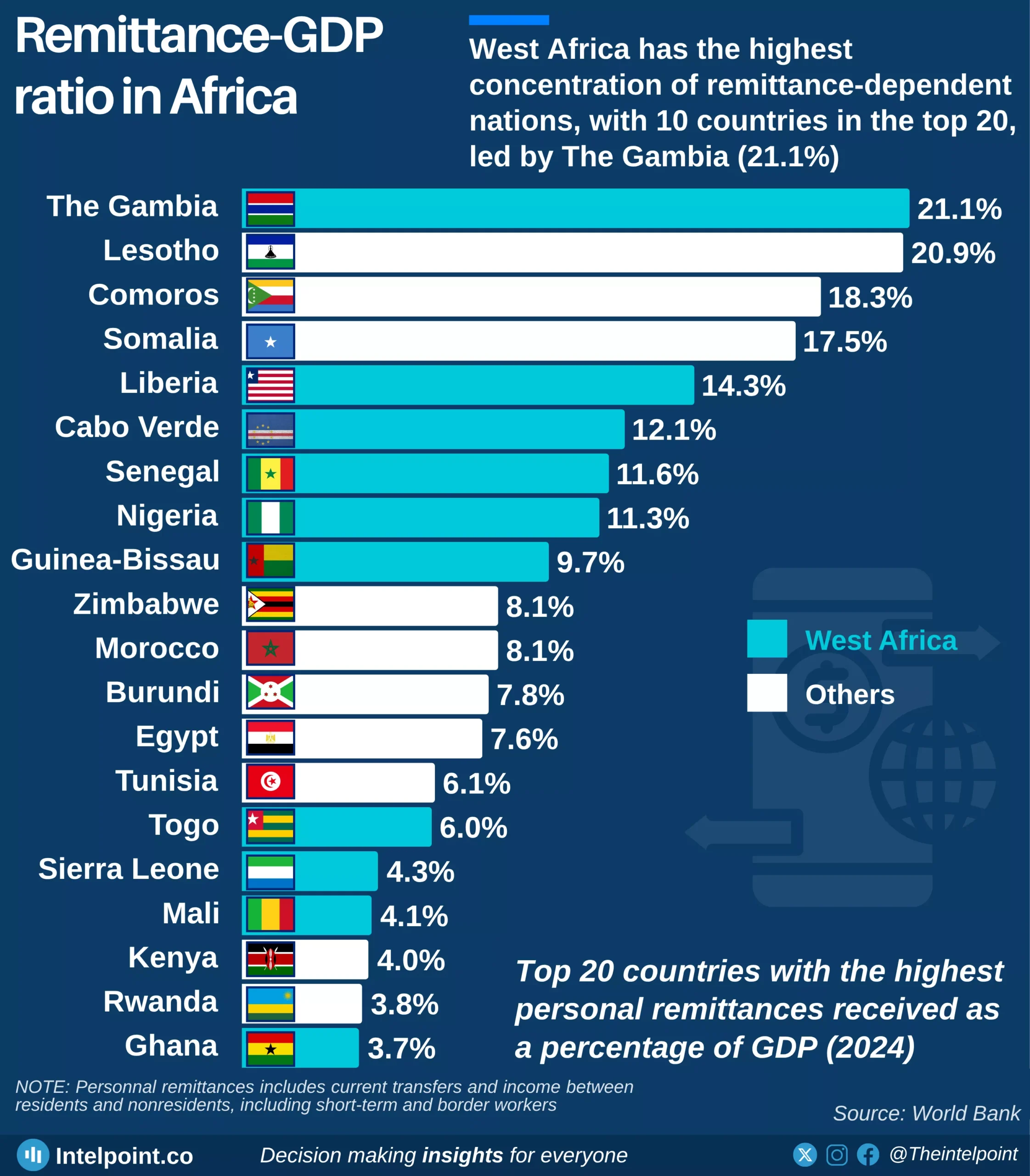
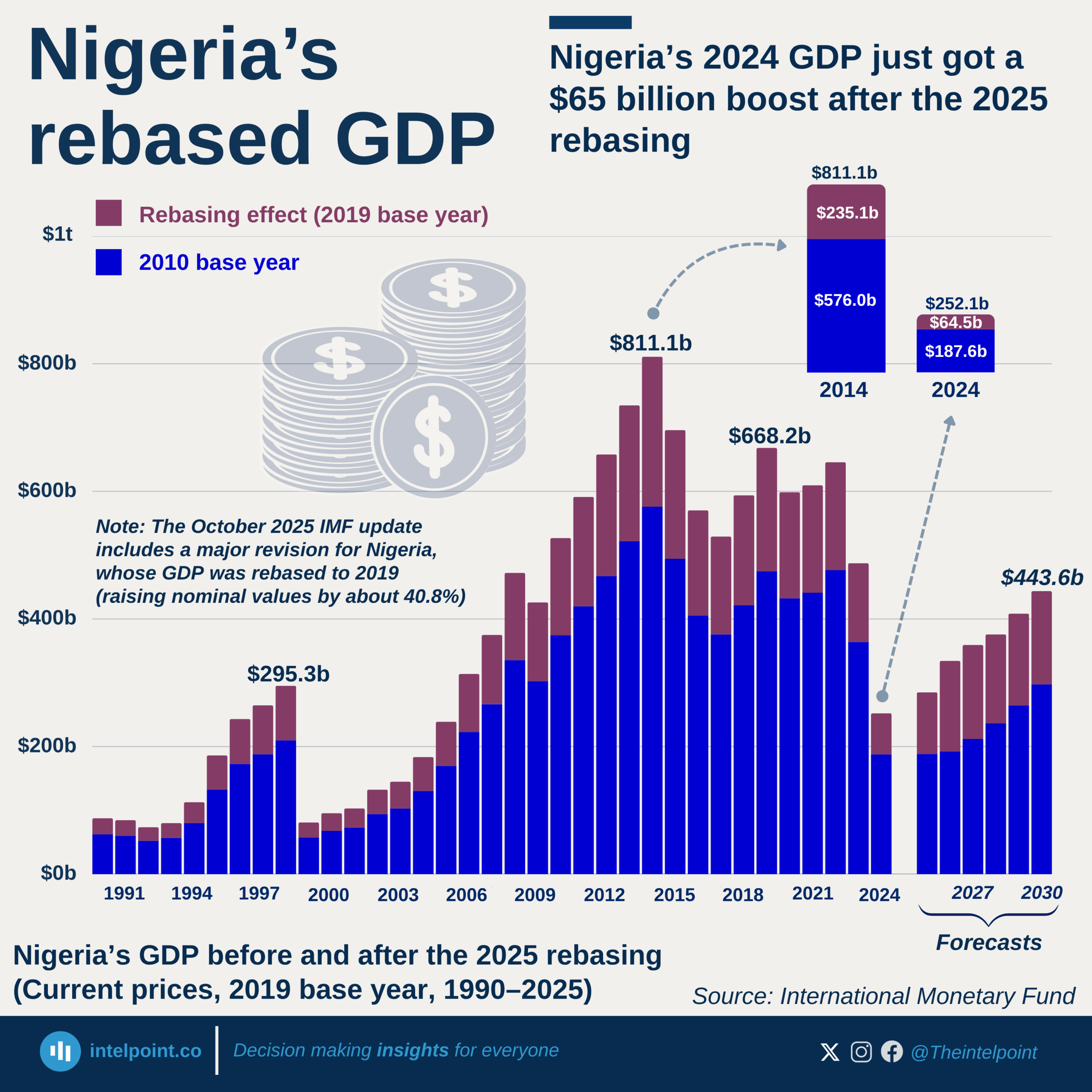
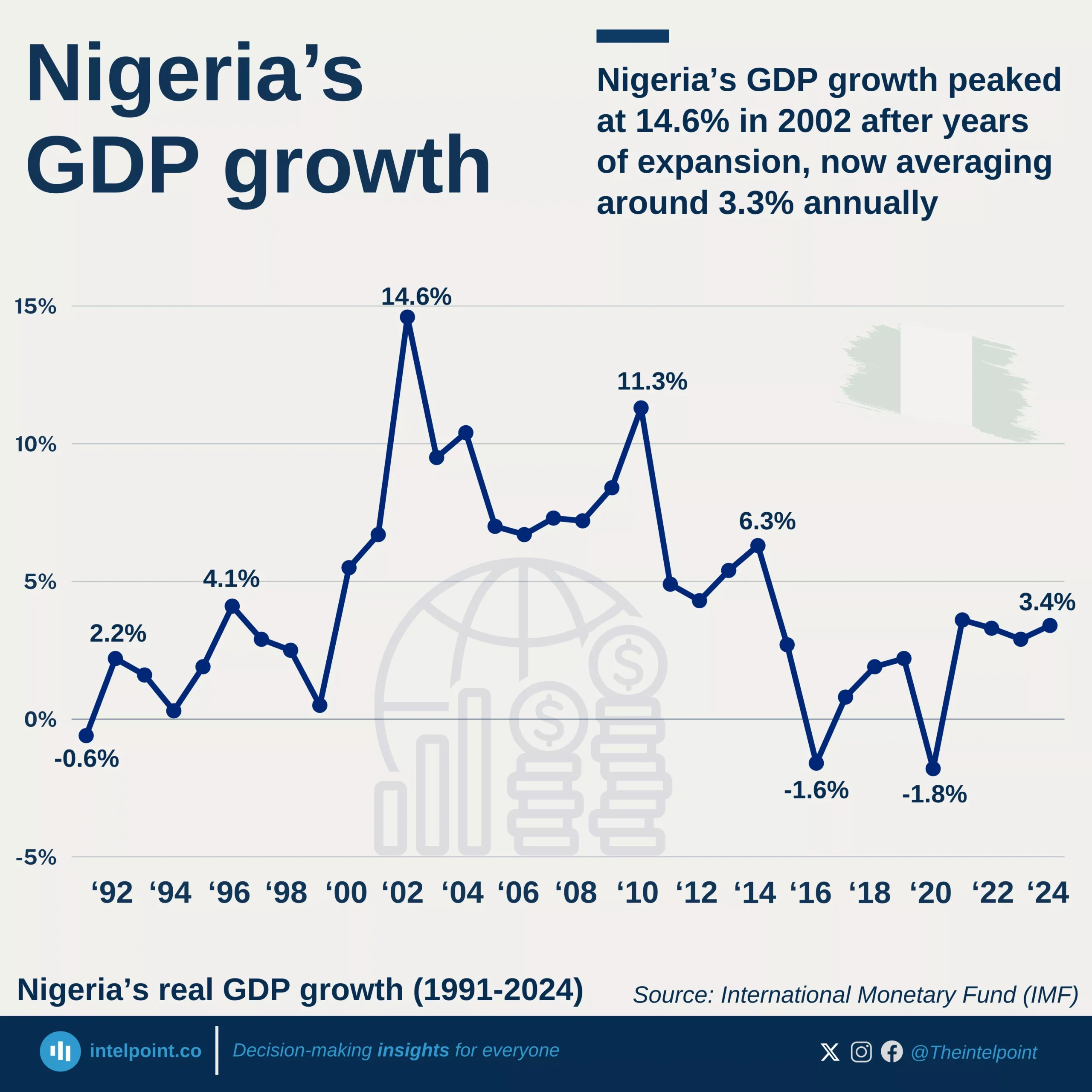
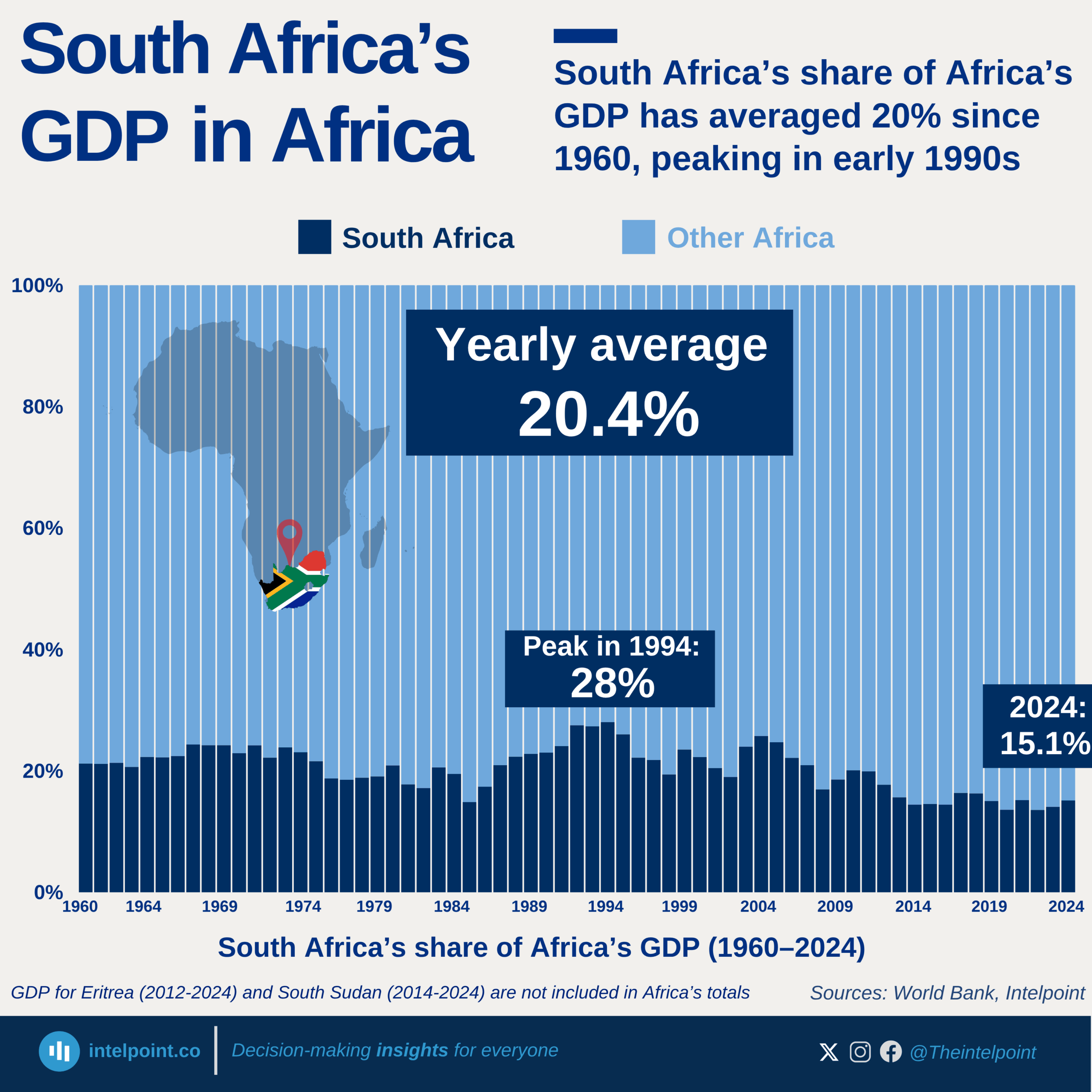
The industrial sector has more than doubled its contribution to GDP with a 20.1% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The services remain the dominant sector, growing at 14.6% CAGR. Meanwhile, agriculture has grown steadily at 11.2% CAGR, highlighting its consistent but slower pace in economic contribution.
The growth of Industry is an evident result of increasing investments in factories and infrastructure that is impacting the different aspects of the country's economy including employment. More young people are now moving from farms to factories, seeking better wages and skills in manufacturing and construction.