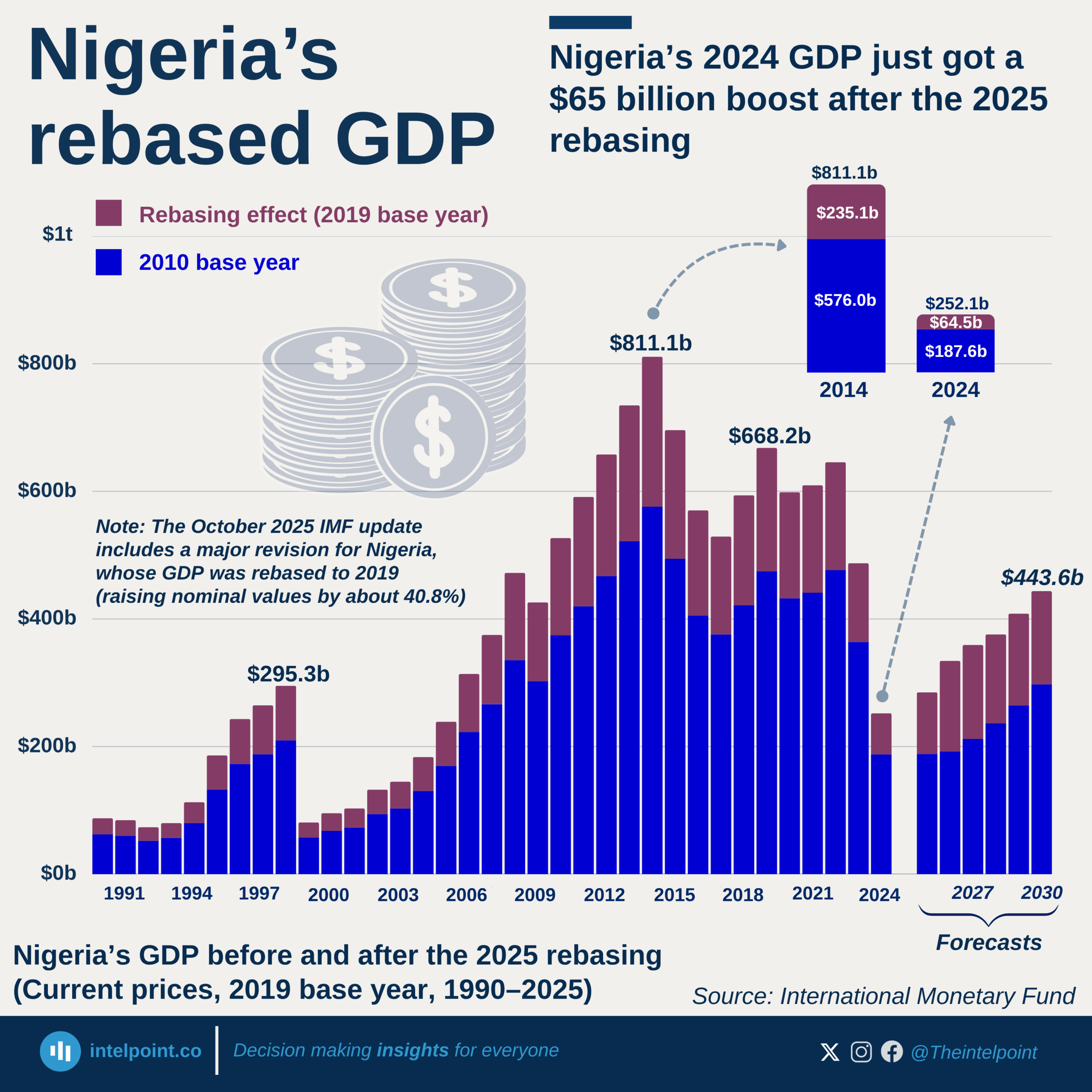
We tracked how long it typically takes Nigeria’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) to release Q1 GDP data. Between 2017 and 2024, the Q1 report was released, on average, 53 days after the end of March, typically around late May.
But 2025 has broken that pattern. As of June 25, the Q1 2025 GDP data is still missing, now 86 days and counting since the quarter ended—33 days later than the usual timeline.
Why the hold-up? Earlier in 2025, the NBS carried out a long-awaited GDP rebasing, adopting 2019 as the new base year. This update is meant to better reflect Nigeria’s evolving economy by capturing newer sectors and providing a more accurate picture of output. That complexity may explain the delay, but it also raises questions about transparency and consistency in national data releases.