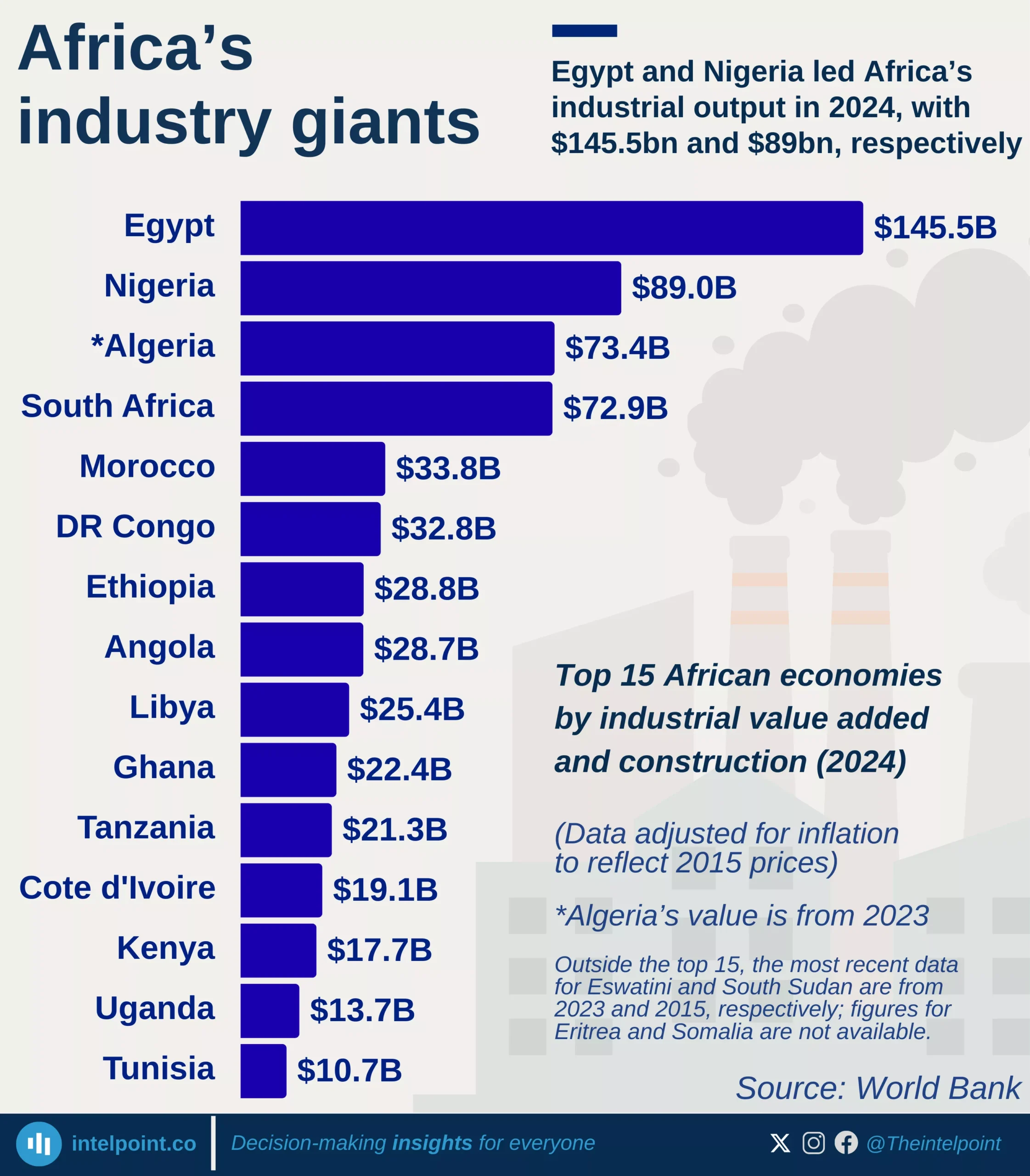
Between 2020 and 2024, Nigeria recorded the sharpest decline in nominal GDP per capita among Africa’s top 10 economies, with a -16.02% annual contraction. While most of the other African top economies managed moderate to strong gains in their citizens’ average economic wellbeing, Nigeria moved in reverse.
Similarly, on average, Egypt experienced a decline in its GDP per capita during the period. Meanwhile, countries like Angola and Algeria saw constant annual growth rates of over 8%, significantly improving the average economic situation of their people. This shows that GDP growth alone isn’t enough — how that growth is distributed and sustained over time also matters.