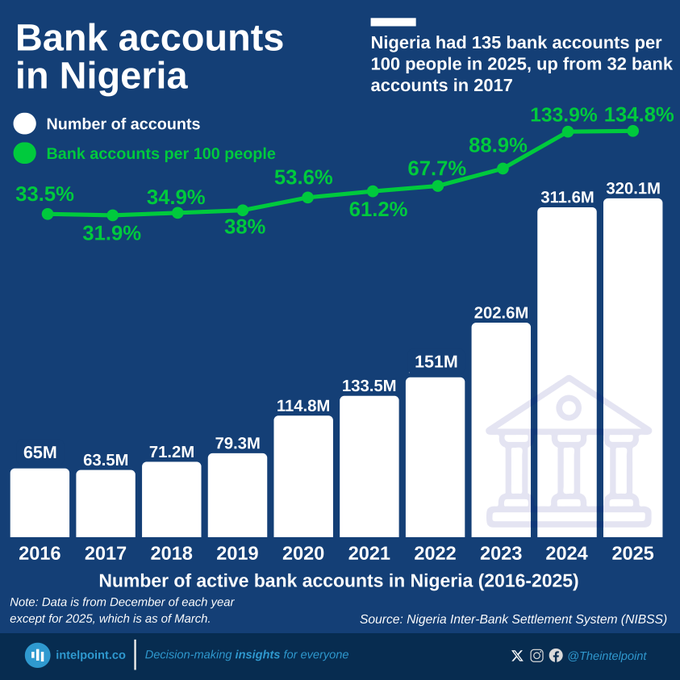
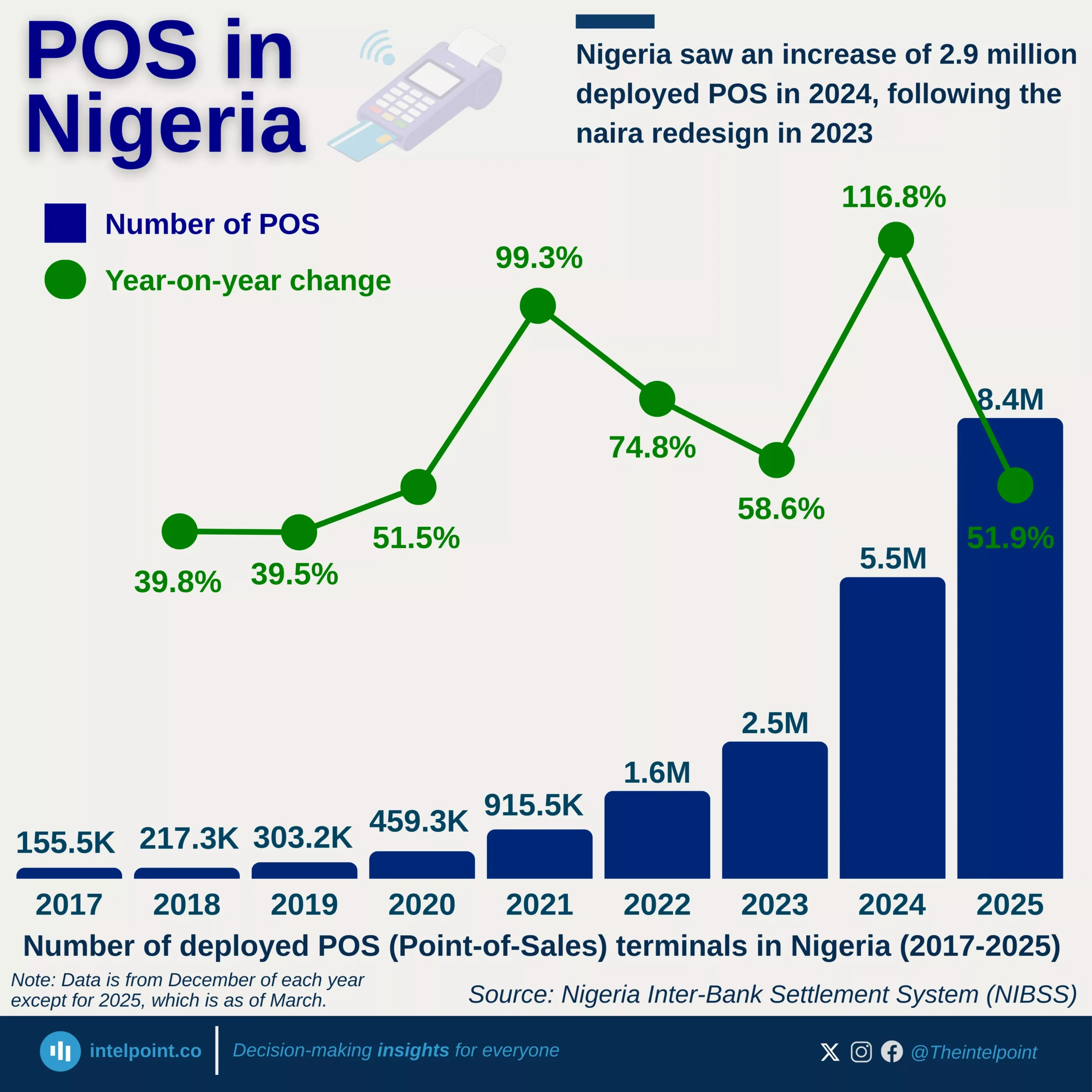
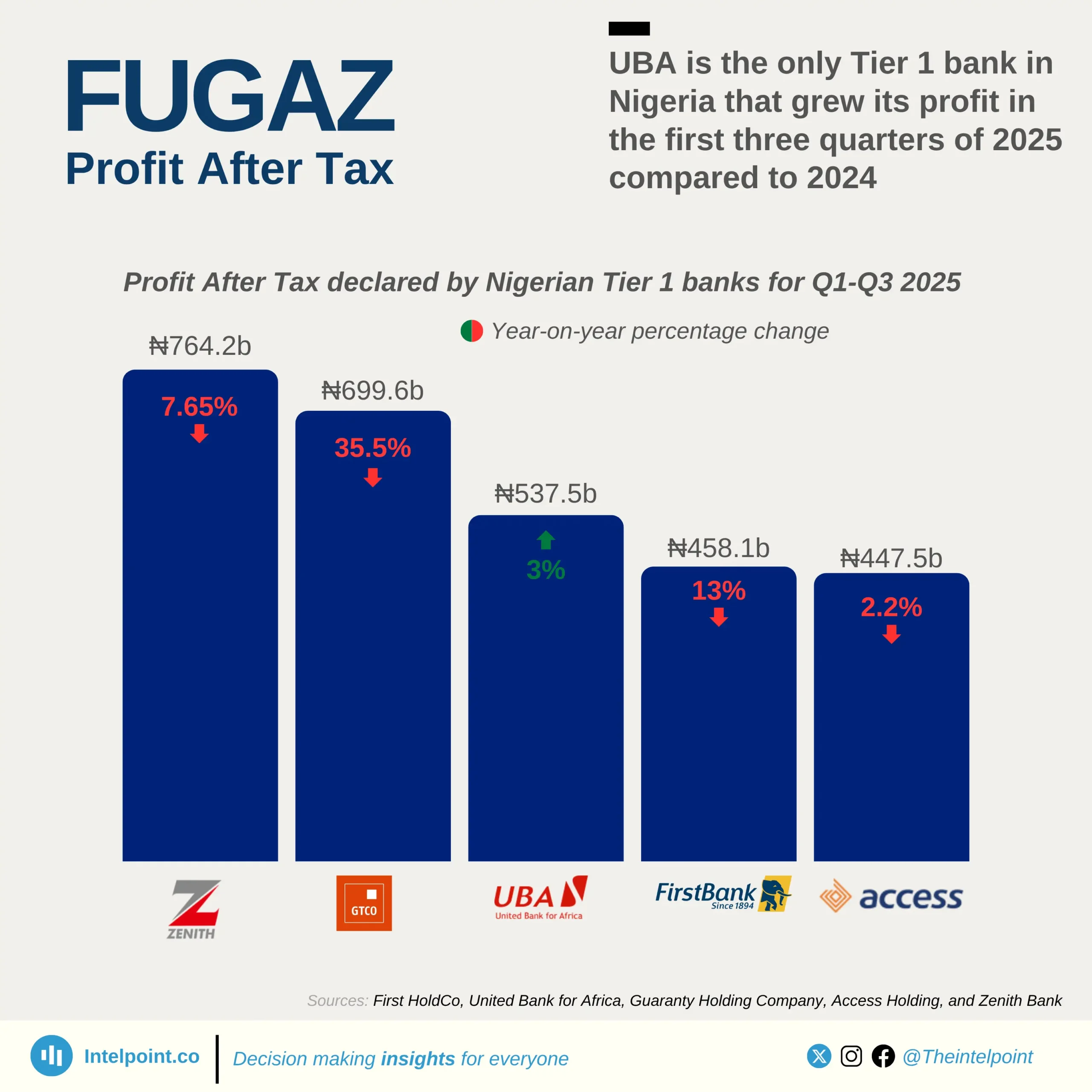
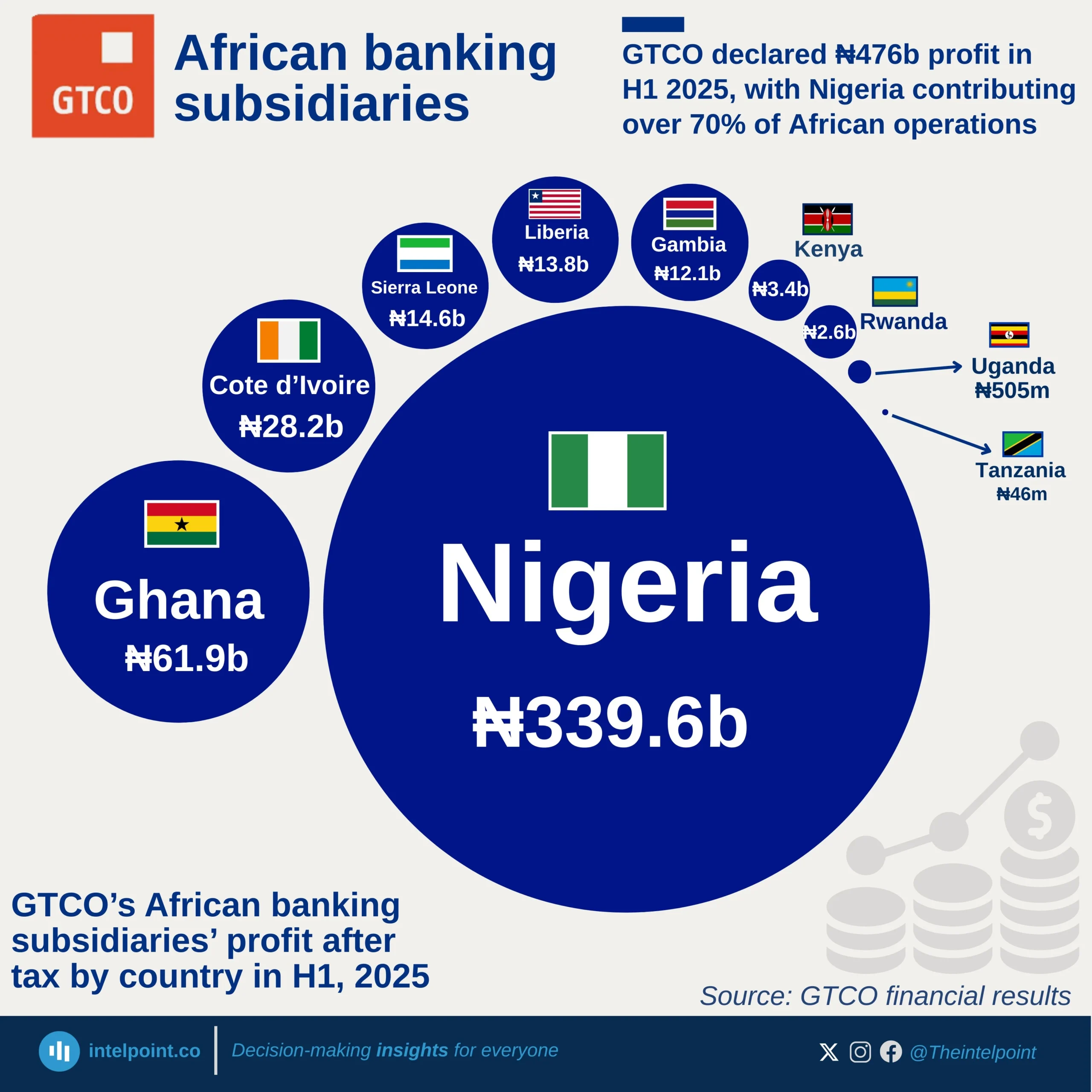
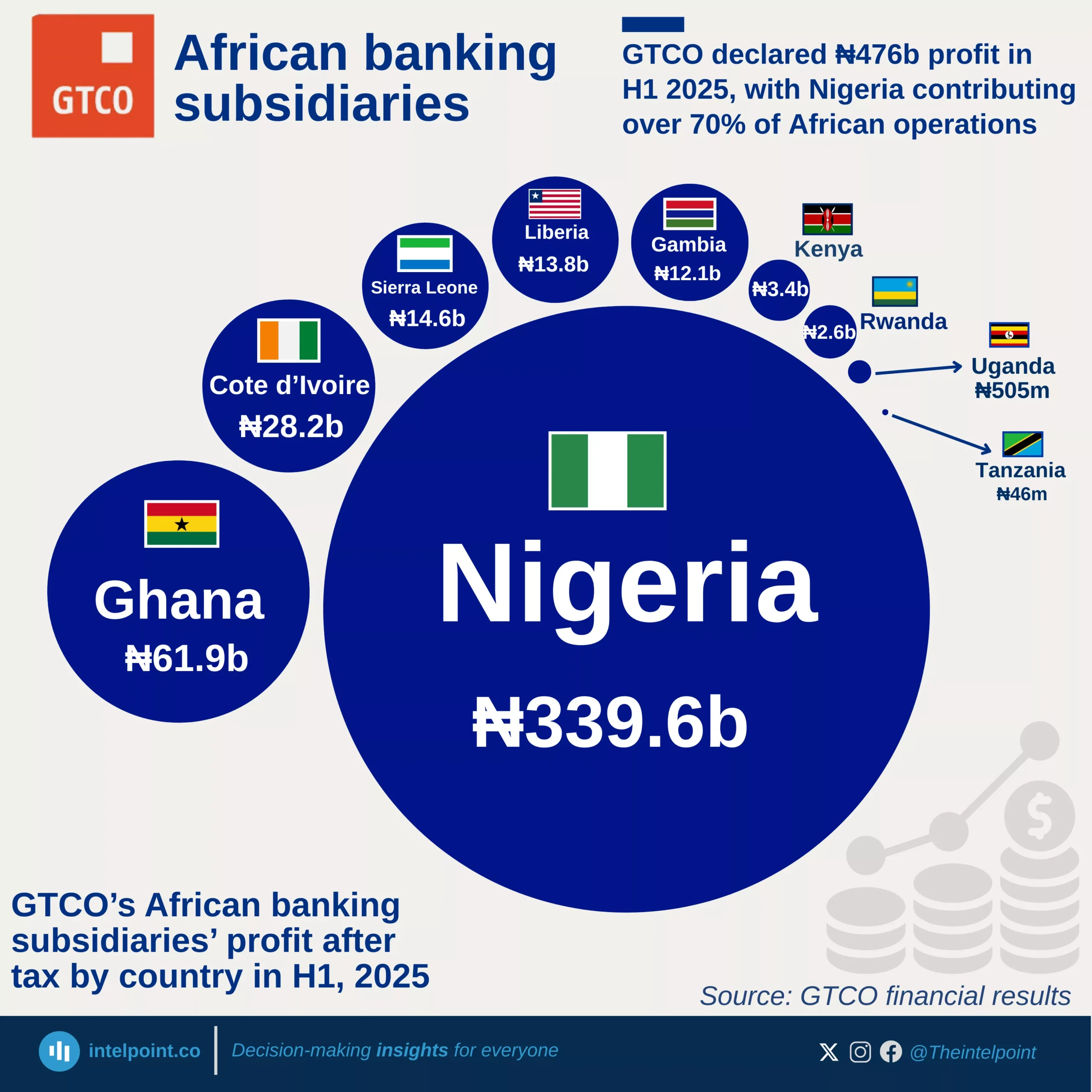
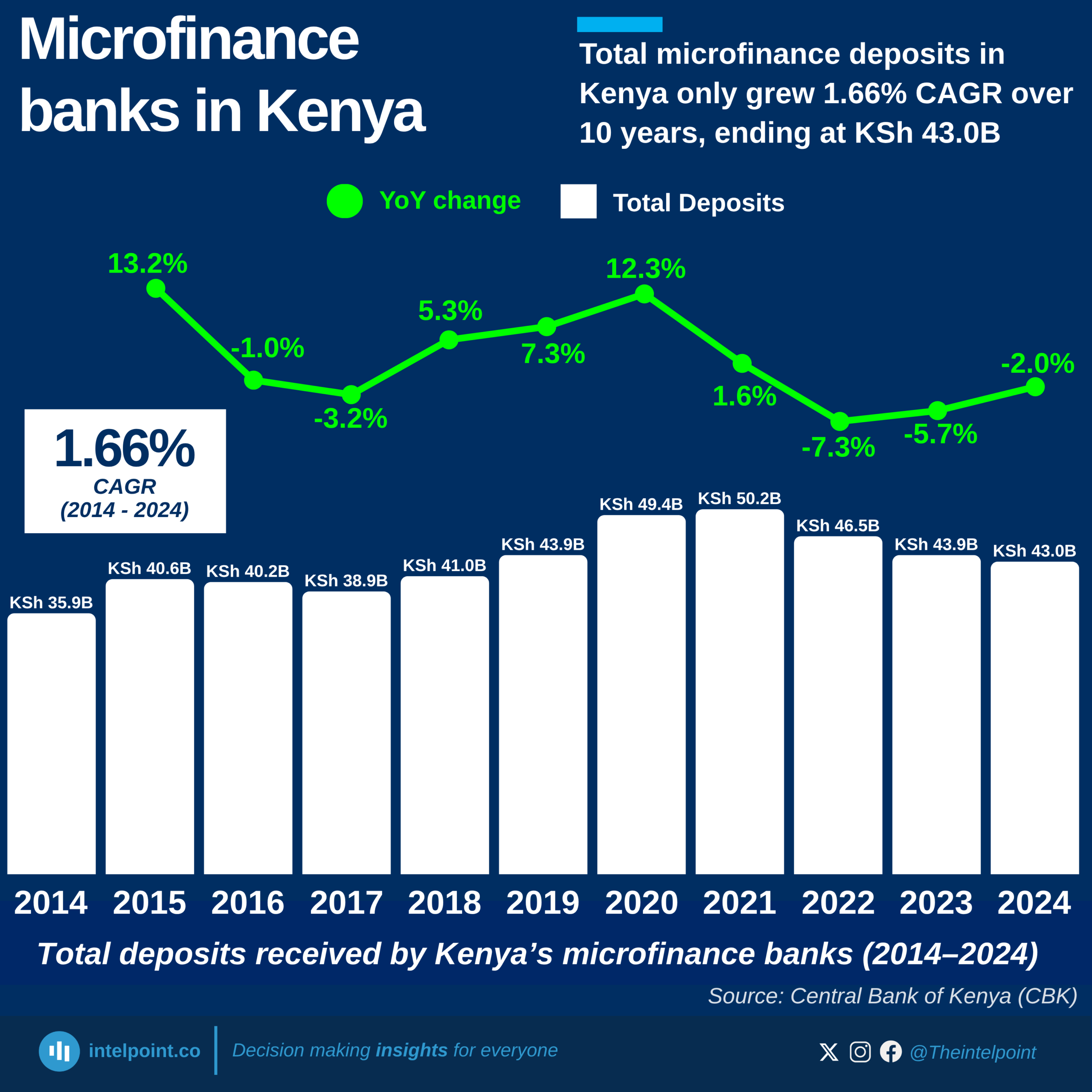
In 2017, Keystone Bank was sold to private investors, marking its transition from state ownership. Over time, it divested from its international subsidiaries, refocusing on the Nigerian market. However, by 2024, the CBN dissolved the board and management of three banks, including Keystone Bank, for non-compliance with sections of the banking legislation.