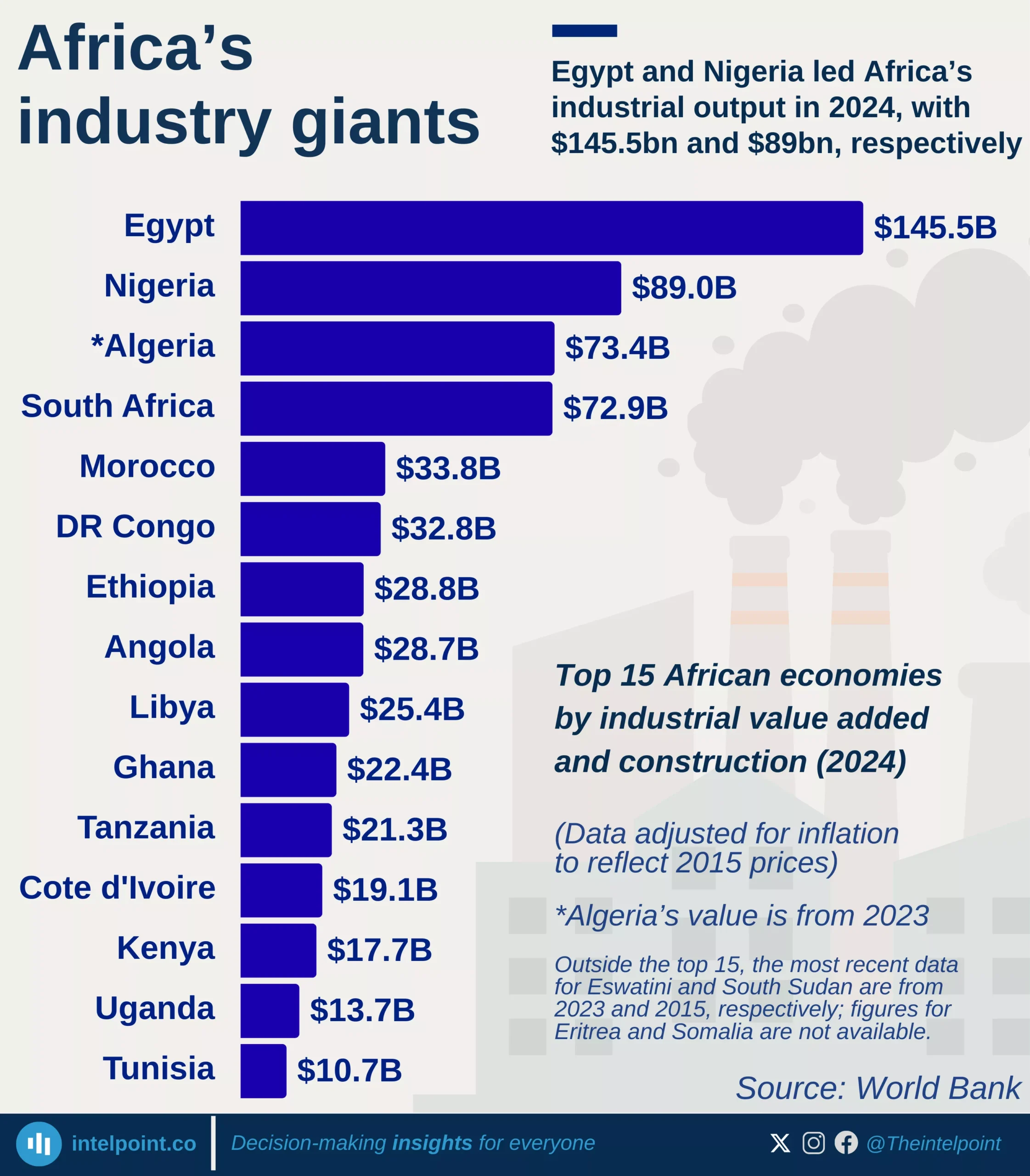
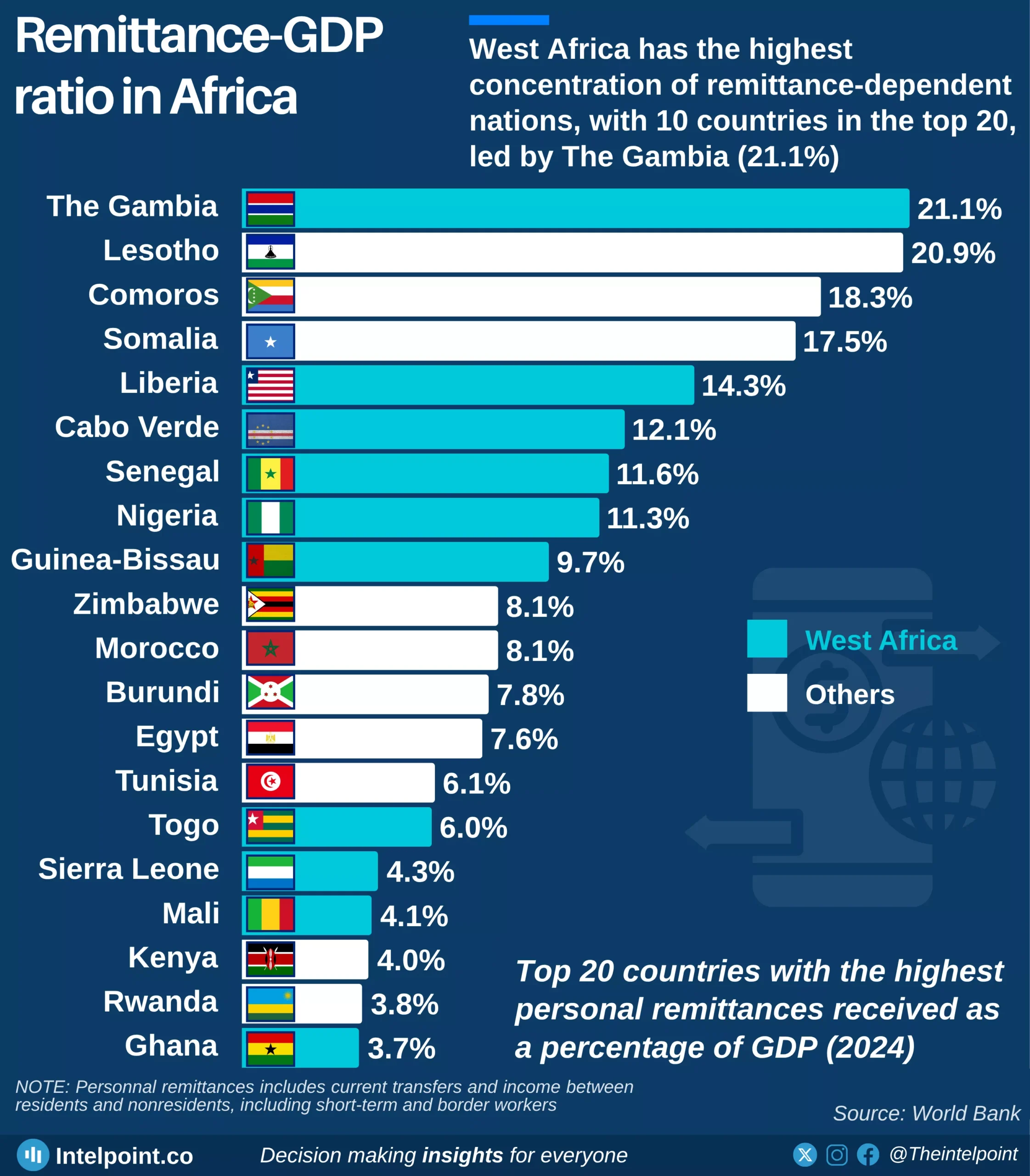
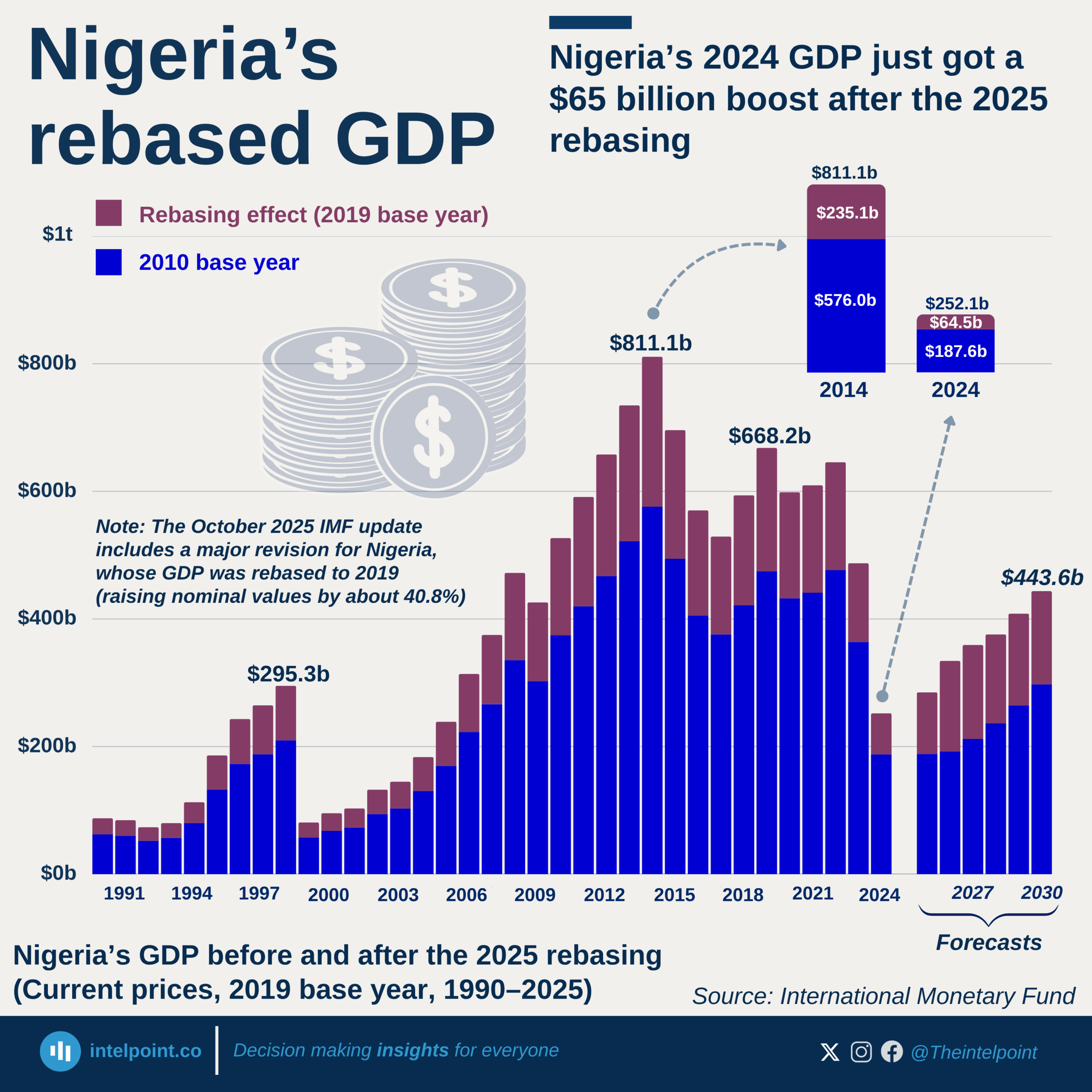
The rebased data breakdown for 2024 offers a dual perspective on Nigeria's economic performance, highlighting both the sectors contributing the most in terms of overall value and those experiencing the most significant growth.
Among the largest contributors to Nigeria's rebased 2024 GDP, Agriculture stands out with ₦59.31 trillion, firmly establishing its foundational role. Following closely are Trade (₦37.81 trillion), Real estate (₦28.96 trillion), and Information and communication (₦20.87 trillion), all demonstrating substantial economic weight.
Concurrently, the economy also showcases dynamic growth in specific areas. Administrative & support services recorded the most impressive percentage increase at 21.07%, indicating a burgeoning demand for specialised business functions. Other top-growing sectors include Arts, entertainment and recreation (8.83%), Water supply, sewerage, waste management and remediation (8.60%), and Transportation and storage (7.92%).
While these high-growth sectors may not yet contribute the largest absolute amounts to the GDP, their rapid expansion signals emerging areas of strength and diversification within Nigeria's rebased economy.