African startups raised $2.2 billion in funding in 2024, down 25% from $2.9 billion the previous year. This total accounted for 0.6% of global startup funding in 2024, reflecting a considerable funding gap. Despite the decline, the second half of 2024 saw a big surge, with $1.4 billion raised, nearly double the $780 million in the first half. Kenya led the funding tables with $638 million, ahead of South Africa, Nigeria, and Egypt. Fintech dominated, raising 43.9% of overall funding, while CleanTech and Mobility also gained traction.
Here’s a detailed table summarising the trends of funding to African startups from 2000-2024:
| Period | Key Trends |
| 2000-2005 | Limited funding activity, with sporadic early-stage venture investments. |
| 2006-2010 | Gradual increase in venture capital; Nigeria, South Africa, Egypt, and Kenya emerged as key markets. |
| 2011-2015 | A significant increase in funding, especially in fintech and technology. |
| 2016-2020 | Further expansion took centre stage, embracing digital transformation. In 2020, there were 450 fintech companies in Africa; by 2024, the number had exceeded 1,200. |
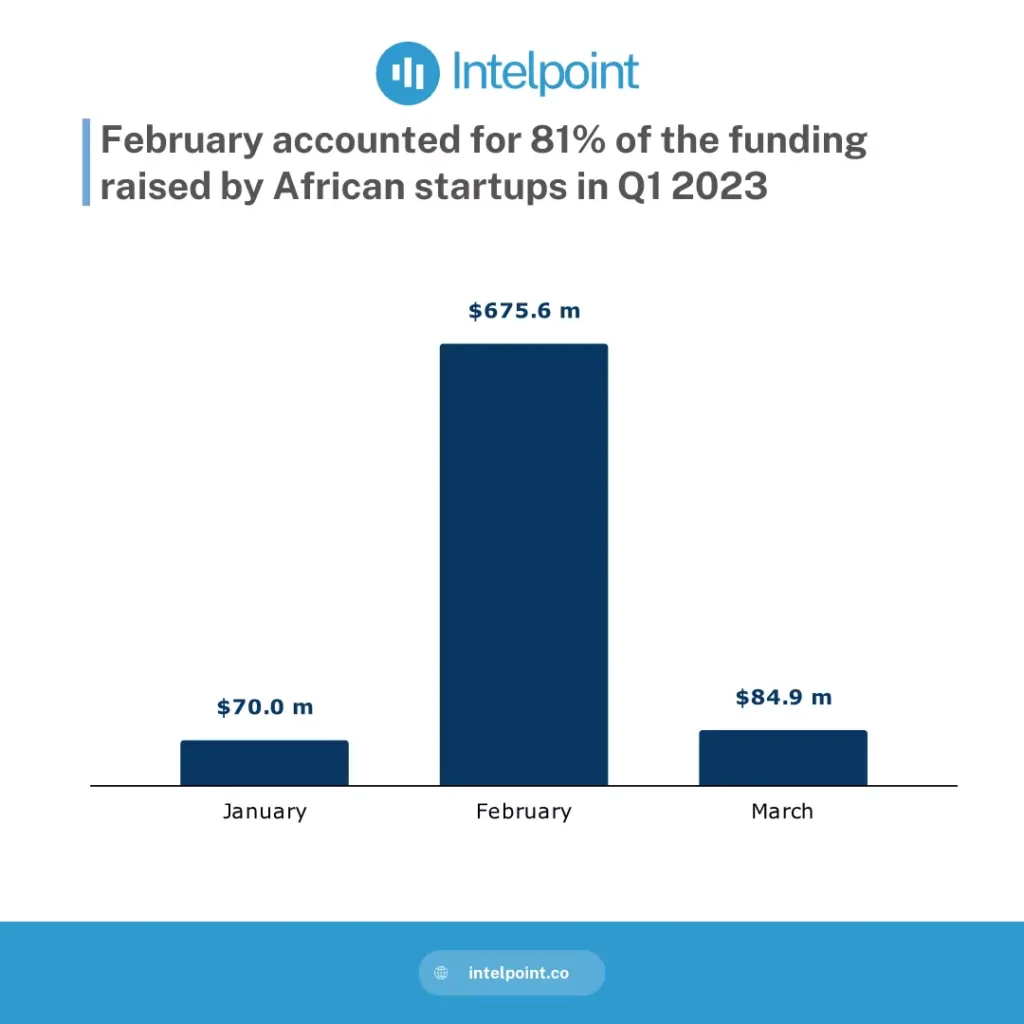
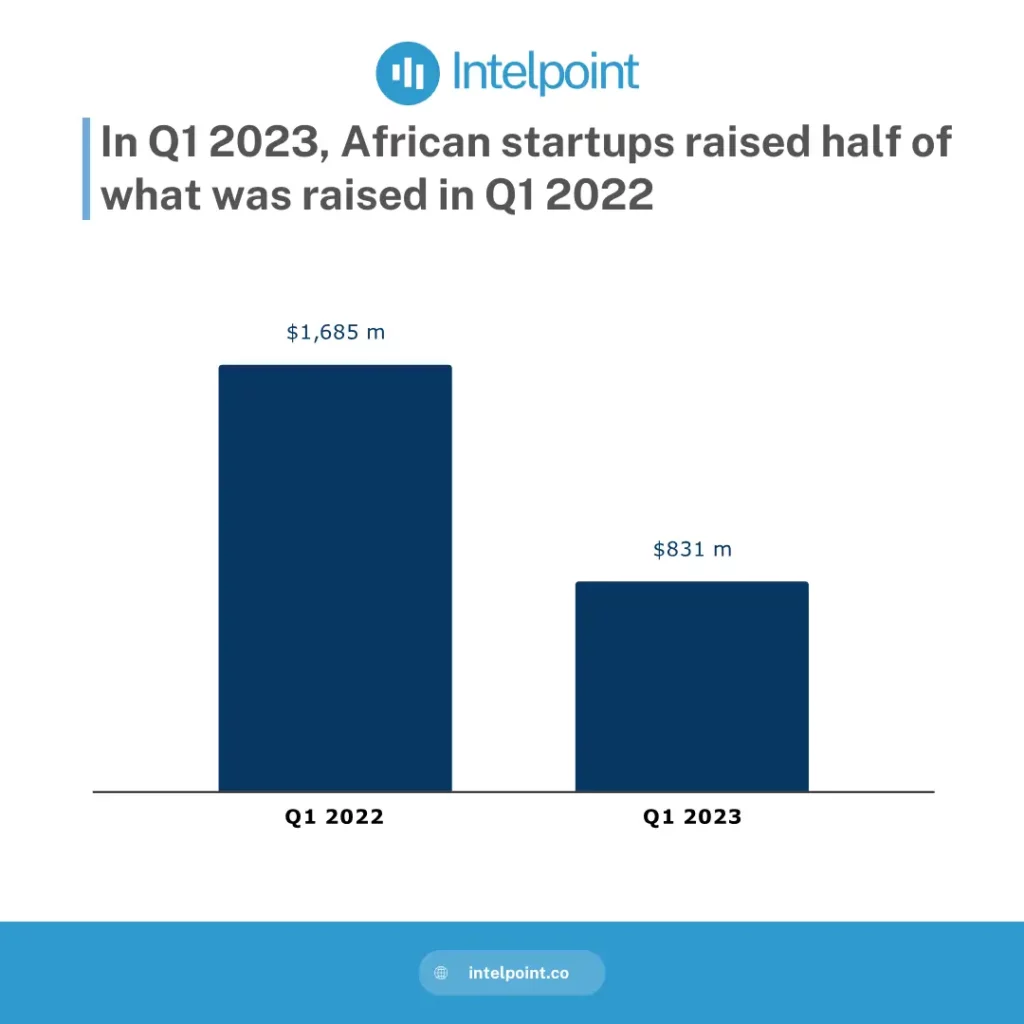
| 2021-2024 | Record funding in 2021 and a decline in 2024 due to global economic factors. In H1 2024, African startups raised about $780M, a drop of 57% in comparison to H1 2023. |
Key takeaways
- 2000-2005: Average yearly financing totalled $50 million, or $250 million for the five years.
- 2006-2010: Venture capital increased to $100 million annually, with Nigeria, South Africa, Egypt, and Kenya taking 70% of investments.
- 2011-2015: Investment grew 500% to more than $1 billion by 2015, with technology and fintech accounting for 60% of investments.
- 2016-2020: Total investment reached $2.02 billion in 2019, up by 130% from 2015, with fintech and healthtech attracting 55% of investments.
- 2021-2024: Startups raised $4.3 billion in 2021, which declined by 49% to $2.2 billion in 2024, with fintech drawing 43.9% of funding.
Trends of funding to african startups from 2000-2024
2000-2005: Emergence of the African startup ecosystem
Annual investment in startups in Africa averaged $50 million, totalling $250 million over the five years. Fixed-line subscribers in Sub-Saharan Africa numbered approximately 8.1 million in 2000 and 9.5 million by 2005, an increment of 1.4 million.
Mobile subscribers rose from 10 million in 2000 to over 110 million in 2006. Internet penetration was less than 1% in 2000, compared to mobile penetration of approximately 2%. By 2005, mobile penetration had increased significantly, but fixed-line penetration was low, with most countries at less than 1%.
2006-2010: Gradual increase in funding
Venture capital investment amounted to $100 million annually. Sub-Saharan African mobile penetration grew from 10% in 2006 to 41% in 2010, and Internet penetration increased from 2.1% in 2006 to 5.1% in 2010.
The introduction of SEACOM and EASSy submarine cables in 2009–2010 raised internet penetration by 3–5 percentage points in Eastern and Southern Africa. However, fixed broadband subscriptions remained below 1 per 100 people.
2011-2015: Significant surge in investments
Investments increased from approximately $200 million in 2011 to over $1 billion in 2015, a more than fivefold increase. Sub-Saharan African mobile penetration increased from approximately 50% in 2010 to 80% in 2015.
Internet penetration increased from 5.1% in 2010 to approximately 20% in 2015. Mobile broadband subscriptions accounted for over 90% of internet subscriptions. African internet bandwidth grew 66% per year during this period.
2016-2020: Substantial growth and diversification
Total startup funding in Africa was $2.02 billion in 2019, a significant increase from previous years. Funding in 2020 was around $1.43 billion, a slight decrease from the previous year. By 2020, mobile penetration in Sub-Saharan Africa was over 80%.
Internet penetration went from 20% in 2015 to around 35% by 2020. The number of startups that received funding increased from 125 in 2015 to 311 in 2019, 148% in four years. Fintech and health tech accounted for a significant proportion of investments, with fintech remaining a top beneficiary.
2021-2024: Record-breaking funding and subsequent decline
African startups raised $2.15 billion in 2021, a record at the time. It increased to $3.33 billion in 2022 but reduced to $2.9 billion in 2023 and $2.2 billion in 2024, a 25% drop from 2023. Equity funding contributed $1.5 billion in 2024, and debt financing amounted to $700 million.
Kenya raised the most funding in 2024, at $638 million. The top five startups received 45% of the total budget. Despite the drop, Africa’s startup ecosystem was more resilient than global trends.
Conclusion
Between 2000 and 2024, African startup funding grew from approximately $50 million annually to over $3 billion by 2022. It represents a 6,000% increase, driven by fintech, health tech, and agri-tech. In 2023, funding decreased to about $2 billion, reflecting a 33% drop due to global economic challenges. Despite this decline, the sector remains resilient, with fintech securing 43.9% of total funding in recent years. Continued investment is crucial to sustain this growth trajectory.