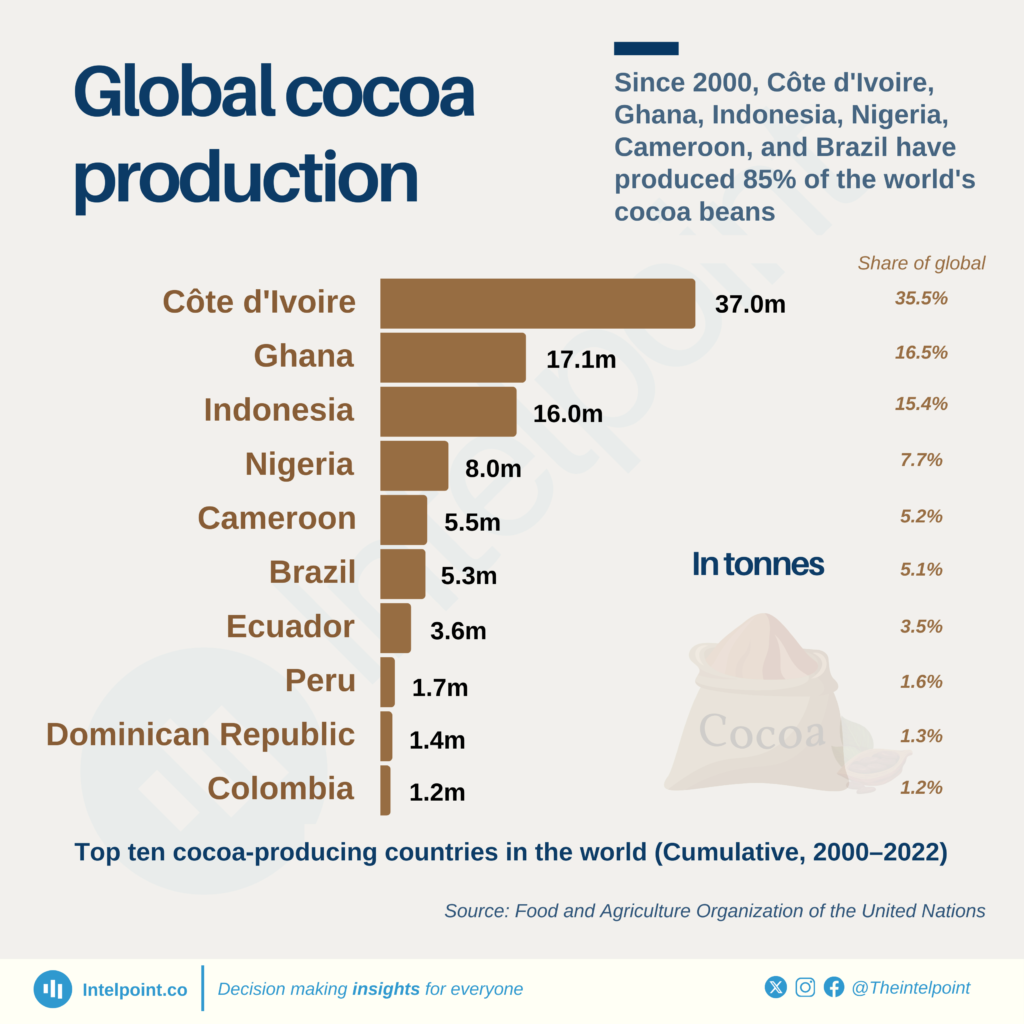
The global cocoa industry is a strong economic engine, with a total trade value of $9.59 billion in 2021. Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana, the world’s two largest cocoa producers, jointly produce over 60% of the world’s total cocoa production. The industry employs millions of individuals, with nearly 600,000 farmers in Côte d’Ivoire and over 3.2 million in Ghana. Nevertheless, it faces deforestation, climate change, and rising input costs.
Here’s a detailed table summarizing the trends of the top ten cocoa-producing countries in the world from 1990-2024:
| Period | Top Countries | Key Trends |
| 1990s | Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Indonesia | Côte d'Ivoire emerged as the leading producer, with Ghana and Indonesia contributing significantly. |
| 2000-2010 | Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Indonesia, Nigeria, Cameroon | The continued dominance of Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana, along with Nigeria and Cameroon, increased their production. |
| 2011-2020 | Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Indonesia, Nigeria, Ecuador | Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana maintained top positions, while Ecuador showed notable growth. |
| 2021-2024 | Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Ecuador, Nigeria, Cameroon | Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana remained the leading cocoa producers, with Ecuador's production continuing to rise. |
Key takeaways
- 1990s: Global average yearly cocoa output was 2.5 million metric tons, of which Côte d’Ivoire produced 800,000 metric tons and Ghana 400,000 metric tons, over 50% of the world's production.
- 2000-2010: Global production amounted to 3.5 million metric tons, led by Côte d’Ivoire (1.2 million) and Ghana (700,000), with Africa accounting for 69%.
- 2011-2020: The global average production was over 4 million metric tons, with Côte d’Ivoire producing 2 million metric tons and Ghana 900,000 metric tons.
- 2021-2024: Overall production plateaued at 4.5 million metric tons, with Côte d’Ivoire contributing 2.2 million metric tons and Ghana 1.1 million metric tons.
Trends of the top ten cocoa-producing countries in the world from 1990-2024
1990s: Foundation of cocoa production dominance
In the 1990s, the world's average cocoa annual production was 2.5 million metric tons. Côte d'Ivoire produced 800,000 metric tons (32%), Ghana 400,000 metric tons (16%), and Indonesia, Nigeria, and Brazil each produced 200,000-300,000 metric tons.
Africa accounted for 69% of the world's production. Ghana's cocoa farms covered 800,000 hectares, and productivity stood at 404 kilograms per hectare. Over 2 million West African farmers relied on cocoa farming. The global cocoa market was valued at $2.5 billion.
2000-2010: Expansion and emerging players in the cocoa industry
Total world cocoa production amounted to about 3.5 million metric tons per year. Côte d’Ivoire topped the list with over 1.2 million metric tons, representing about 34% of the world’s production.
Ghana’s output rose to some 900,000 metric tons in 2010, compared with 450,000 metric tons in 2000. Indonesia became a significant producer, with about 500,000 metric tons yearly, or around 14% of the world’s production. Africa produced about 68% of the world’s output, and the Far East about 18%.
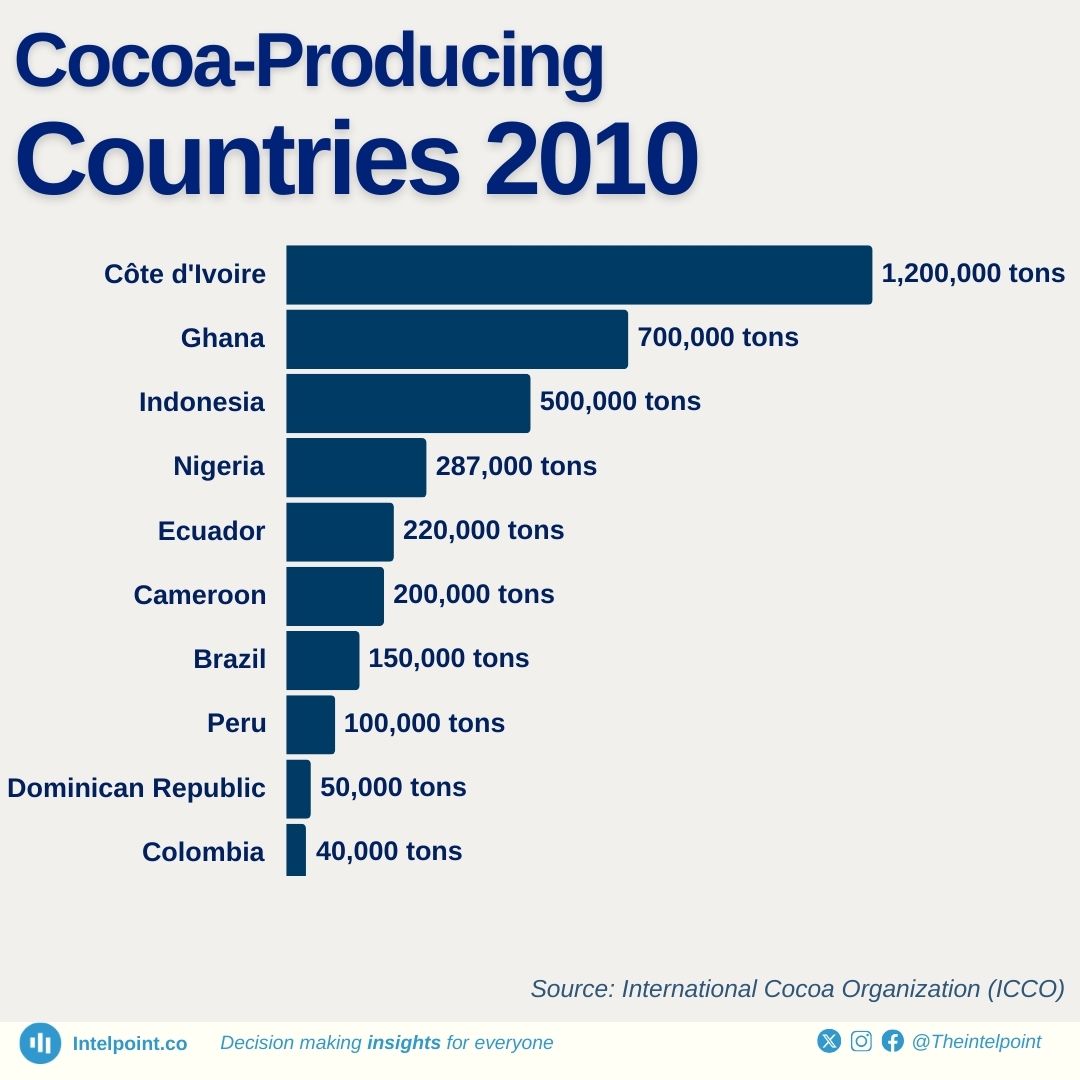
2011-2020: Continued growth amidst challenges in cocoa production
The world's cocoa production averaged more than 4 million metric tons annually. Côte d’Ivoire harvested 2 million metric tons, approximately 40% of the world's output. Ghana harvested 900,000 metric tons per year. Indonesian production decreased to 300,000 metric tons due to disease and old plantations.
Nigeria harvested 250,000 metric tons annually, and Ecuador's production increased to more than 200,000 metric tons yearly. Africa supplied 70% of world production, with West Africa supplying 60%. The world market for cocoa was around $9 billion a year.

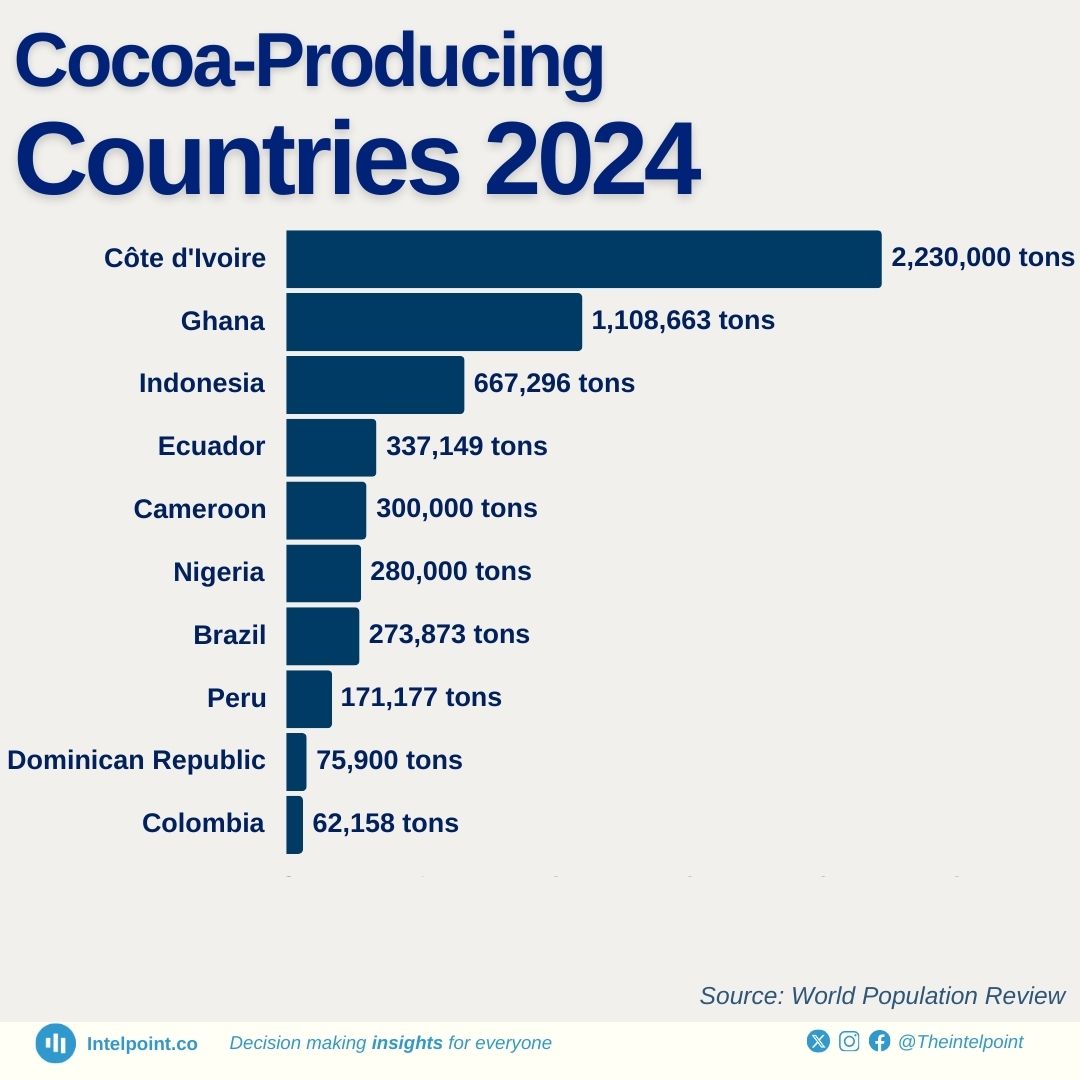
2021-2024: Recent trends and future outlook in the cocoa market
Global cocoa production leveled off at about 4.5 million metric tons annually but fell to 4.382 million in the 2023-24 crop year. Côte d'Ivoire produced 2.2 million metric tons annually, and Ghana averaged 1.1 million metric tons annually.
Ghana's production, however, plummeted in the 2023-24 crop year to less than 55% of its average. Ecuador's production amounted to around 330,000 metric tons a year. Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana produced almost 60% of the world's total. World cocoa prices rose by 157% in 2024 based on supply worries.
Conclusion
Over the past three decades, global cocoa production increased from approximately 2.5 million metric tons in the 1990s to over 4.5 million by 2024. Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana produce approximately 60% of the global output. Côte d’Ivoire produced 2.2 million metric tons in 2022, while Ghana produced 1.1 million metric tons. Recent setbacks due to climate change and disease have impacted production, with Ghana posting a 40% deficit and Côte d’Ivoire anticipating a 30% decline in 2024.
FAQs
What are the top 10 cocoa producing countries in the world 2024?
The top 10 cocoa-producing countries in the world in 2024 are Ivory Coast, Ghana, Indonesia, Ecuador, Cameroon, Nigeria, Brazil, Peru, the Dominican Republic, and Colombia.
What is the market trend for cocoa?
In 2024, the price of Cocoa was highly volatile and reached an all-time high. In December 2024, it reached $12,906 per metric ton due to a supply shortage in major producing regions like West Africa.
Which country is the highest producer of cocoa in the world?
The Ivory Coast remains the world's leading cocoa producer, accounting for more than 30% of global production, with about 2.2 million tonnes annually.
Where is cocoa mostly grown in Nigeria?
In Nigeria, cocoa is predominantly grown in the southwestern region. Key producing states include Ondo, Osun, Ogun, Ekiti, and Oyo, which account for over 60% of the country's cocoa production.