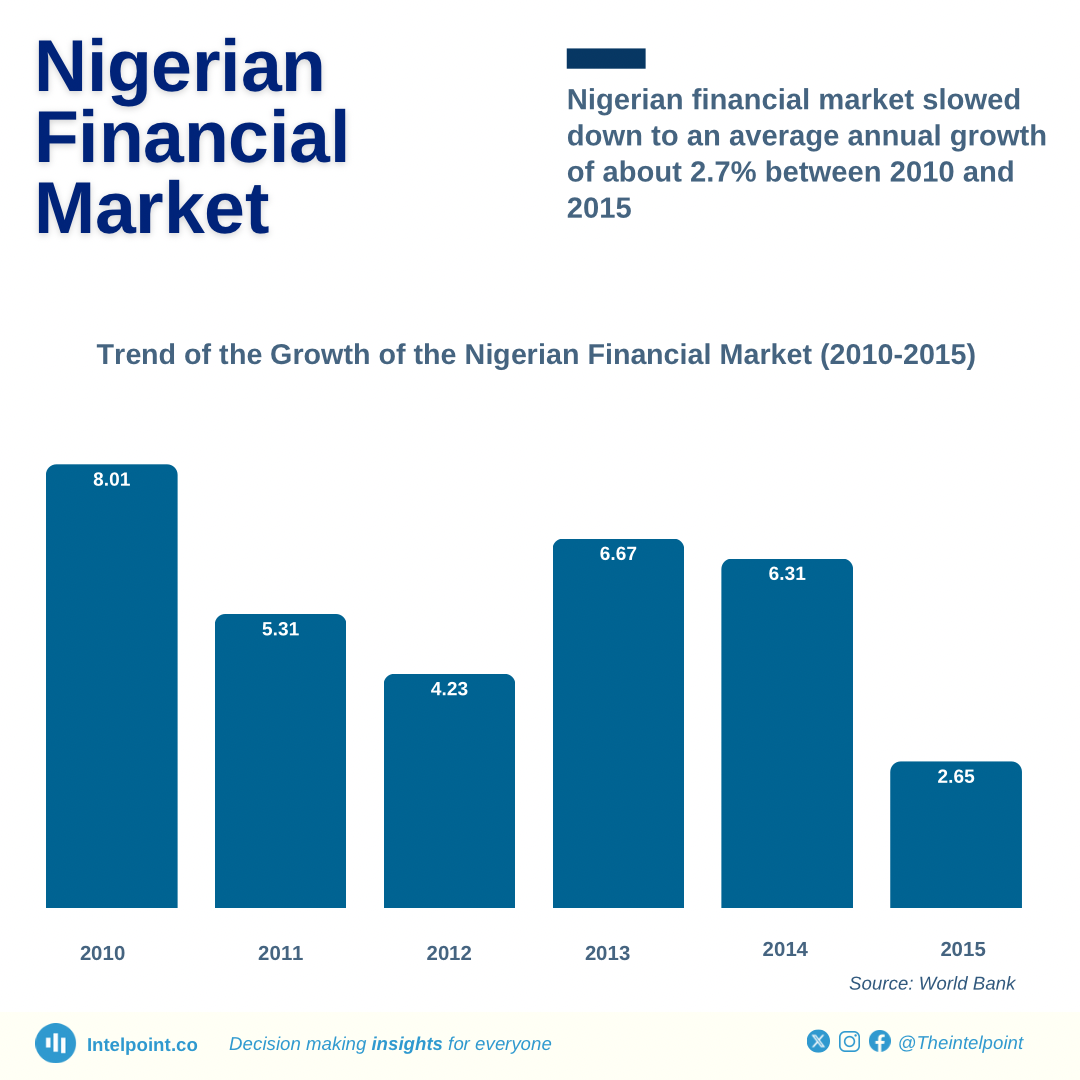
From 2000-2024, the Nigerian financial market grew significantly. Some major statistics include average growth of 6.5% from 2000-2009, 2.7% from 2010-2015, and 0.66% from 2016-2020. GDP growth rose to 3.6% in 2021, 3.2% in 2022, 3.0% in 2023, and 3.46% in Q3 2024. The industry remains paramount even with inflation rates of over 30% and an 18.5% December 2024 Monetary Policy Rate. Banking reforms consolidated banks from 89 down to 25 and enhanced the capital base up to N25 billion, and the capital market also had the luxury of technological advancements.
Here’s a table summarizing the key trends in Nigerian financial market growth (2000–2024):
| Year/Period | Major Events/ Trends | Key Drivers |
| 2000-2009 | The Nigerian economy recorded rapid growth, averaging about a 6.5% annual increase in GDP. | High global oil prices, increased foreign direct investment, and economic reforms. |
| 2010-2015 | This phase has seen the economy slow to an average annual growth of about 2.7%. | Decline in oil prices, reduced foreign investment, and policy uncertainties. |
| 2016-2020 | The recovery phase followed the economy's contraction by 1.61% in 2016. From 2016 to 2020, the economy had an average annual growth rate of about 0.66%, with a contraction of 1.8% in 2020. | Oil price volatility, economic reforms, and global economic conditions. |
| 2021-2023 | The economy rebounded in 2021, with a growth rate of 3.6%, followed by 3.2% in 2022 and 3.0% in 2023. During this time, however, inflationary pressures intensified. | Post-pandemic recovery, increased oil production, and fiscal policies. |
| 2024 | It represents the projected economic growth with fiscal policy support and reform efforts in oil and non-oil sectors for 2024 at a rate of 3.2%. Inflation moderation is forecast at 21.40% of the current rate of increase. | Fiscal policy support, reforms in the oil and non-oil sectors, and infrastructure development. |
Key takeaways
- 2000-2009: The Nigerian economy grew on average 6.5% every year, led by international oil prices and foreign capital.
- 2010–2015: The GDP growth rate has been 2.7% annually, impacted by lower oil prices and lower foreign investment.
- 2016-2020: The economy fell into recession in 2016 with a 1.62% fall, with 0.66% average annual growth for this period.
- 2021-2023: GDP growth rates of 3.65%, 3.25%, and 2.86%, led by the rebound of the oil price and economic diversification.
- 2024: The GDP of Nigeria rose 3.46% in the third quarter, with growth propelled by increased investor activity and digitalization.
2000–2009: Banking reforms and consolidation
From 2000-2009, GDP growth had been 6.5% on average. Banking consolidation and reforms reduced banks from 89 to 25, increased overall banking capital by 439.4%, and increased deposits by 241.8% between 2003-2009. The banks' minimum capital base increased to N25 billion, stabilizing the banking industry.
2010–2015: Post-crisis recovery and foreign investments
Nigeria's GDP grew at an average annual rate of 2.7% from 2010 to 2015. Significant government stimulus policies and improved regulatory environments contributed to this growth.
The economy grew 7.8% in 2010, but growth slowed with the fall in oil prices. Nominal GDP also rose 7.12% in Q4 2015 compared with Q4 2014. Foreign investment also significantly contributed to this growth period.
2016–2020: Recession and technology-driven growth
From 2016-2020, a 2016 recession of 1.61% GDP had occurred. The average annual GDP growth rate of 0.66% had been present. The fintech space had grown significantly, with over 200 fintech operators in Nigeria and fintech investments 197% higher in three years.
2021–2023: Post-pandemic growth
The financial market of Nigeria started to grow again, and its GDP increased by 3.6% in 2021, 3.2% in 2022, and 3.0% in 2023. The services sector contributed significantly towards GDP. The 2023 nominal GDP of Nigeria was $362.81 billion, and 38.9% of its 87 million people were affected by poverty.
2024: Growth amid inflation and global pressures
In 2024, Nigeria’s GDP grew by 3.46% in the third quarter, driven by the services sector, which accounted for 53.58% of GDP and grew at 5.19%. The nominal GDP reached ₦71.13 trillion, marking a year-on-year increase of 17.26%. Inflation rose to a near 30-year high of 34.8% in December 2024. The Monetary Policy Rate was set at 27.5% to combat inflation.
Conclusion
From 2000 to 2024, the Nigerian financial market remained resilient to shocks. Regulatory reforms, technological innovations, and diversification were the forces behind this resilience.
However, some problems remain: inflation increased by 33.2% in March 2024, exchange rate fluctuations caused a 95.6% drop in 2023, and GDP growth dipped to 2.98% in Q1 2024.
FAQs
What is the economic growth rate in Nigeria in 2024?
In the third quarter of 2024, the Nigerian economy grew by 3.46% year over year, largely due to the services sector's over 50% contribution to the GDP.
What is the economic growth rate in Nigeria over the years?
The average annual growth rate of the Nigerian economy from 2000 to 2009 was approximately 6.5 percent; from 2010 through 2015, the actual rate was about 2.7 percent. It grew at an average annual rate of about 0.66% from 2016 to 2020, with a contraction of 1.8% in 2020. In 2021, it rebounded with 3.6% yearly growth, followed by a further 3.2% in 2022 and 3.0% in 2023. The third quarter of 2024 reported a year-on-year increase of 3.46%.
What is the IMF report for Nigeria in 2024?
The IMF projects that Nigeria's real GDP growth will be 2.9% in 2024, while consumer prices are expected to increase by 32.5%.
What is the current interest rate in Nigeria in 2024?
The current Monetary Policy Rate of the Central Bank of Nigeria is 18.5% as of December 2024.