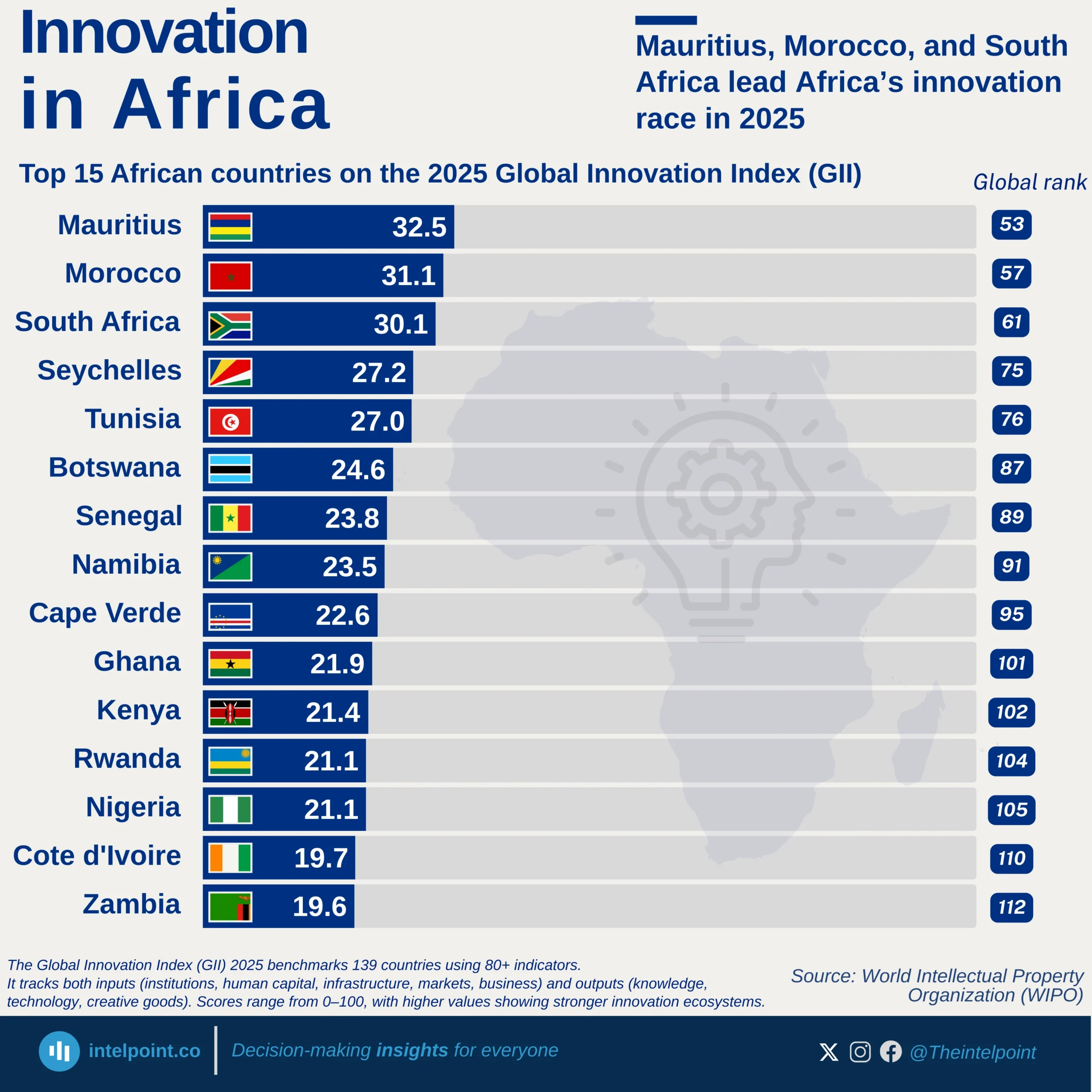
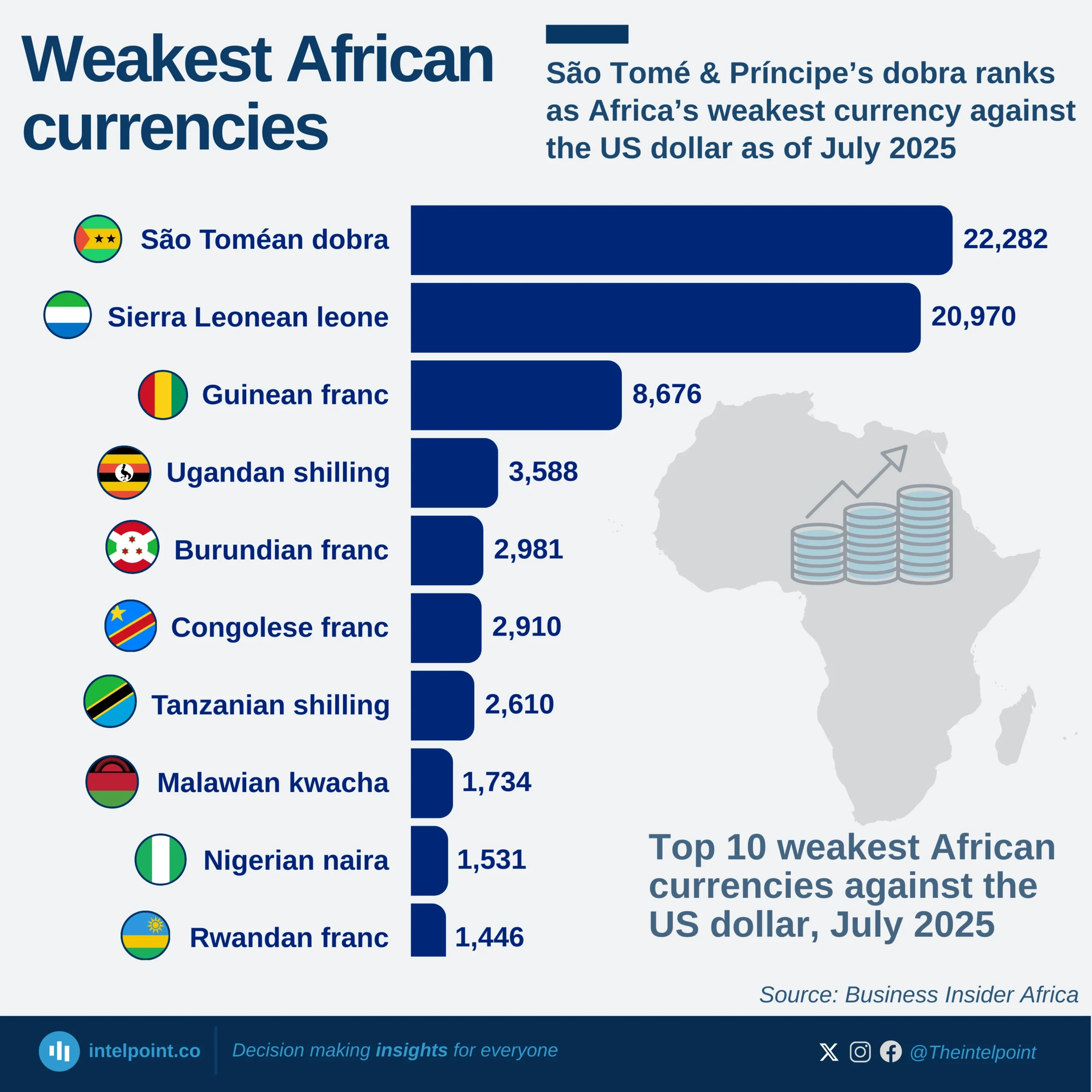
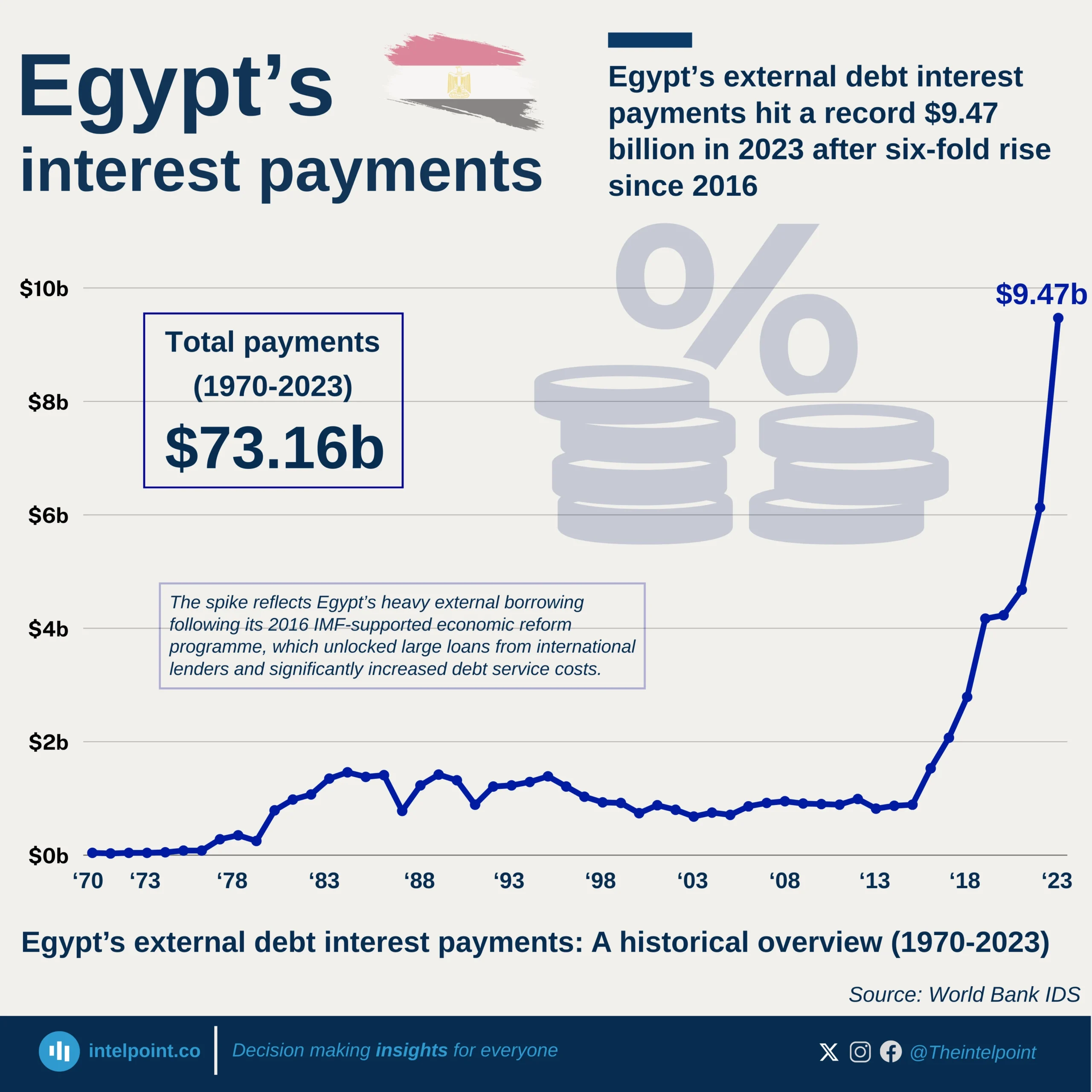
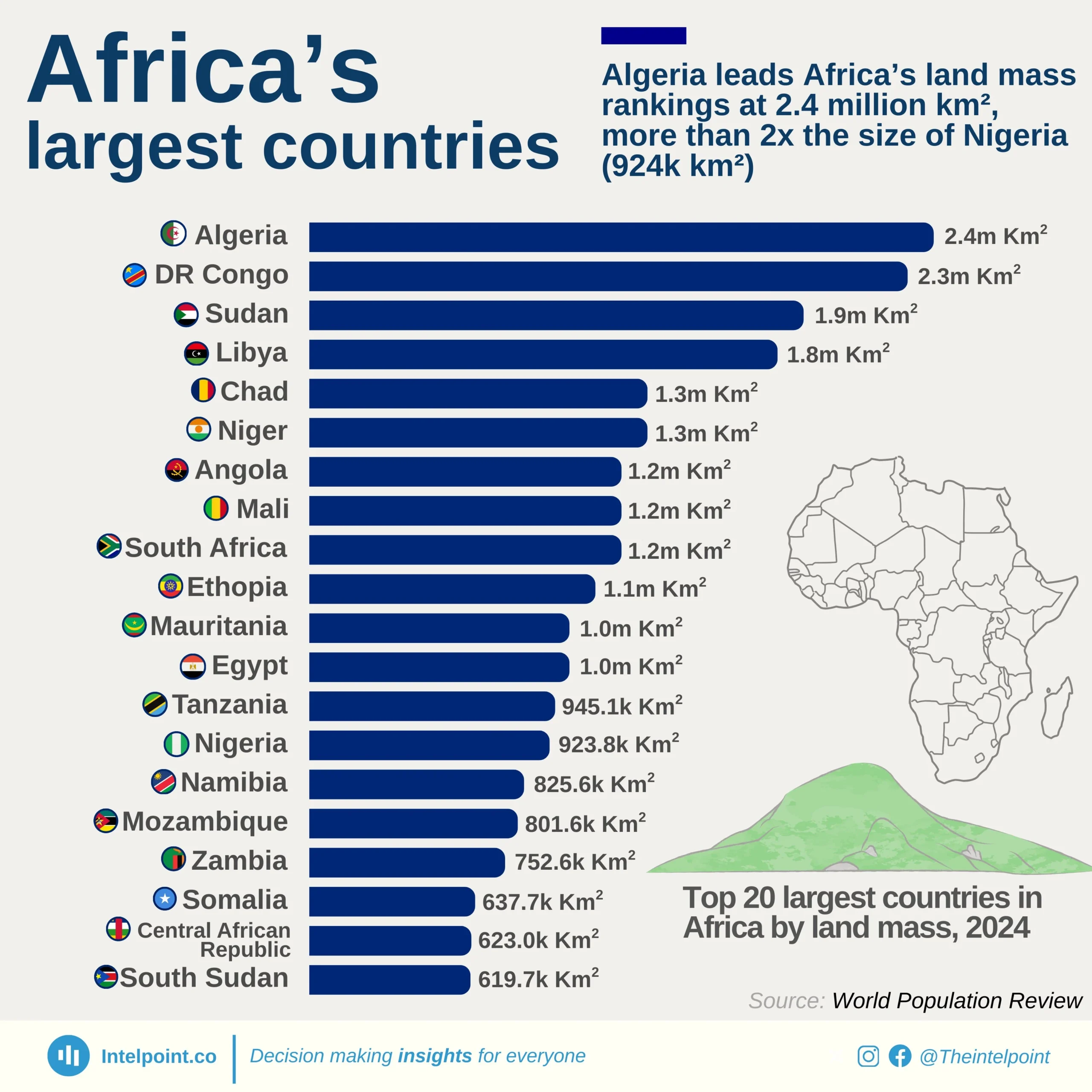
Seychelles stands out as Africa’s top performer in infrastructure development for 2024, achieving an almost perfect score of 99.77 on the African Infrastructure Development Index (AIDI). The chart showcases the leading countries on the continent in terms of infrastructure, with Seychelles not just topping the list but also setting a benchmark that reflects consistent progress across multiple sectors such as energy, transport, ICT, and water. Following Seychelles are Egypt (91.43), Libya (85.84), and Mauritius (82.77), further indicating how Northern and island nations are leading the pack.
For many Africans, especially those in rapidly urbanising areas, stable electricity, reliable transport, and internet access are still not guaranteed. Thus, seeing countries like Seychelles and Mauritius reach such high AIDI scores reflects what's possible when policy, planning, and public investment align. These scores translate into tangible improvements—shorter commutes, better water access, and stronger digital infrastructure—realities that millions across the continent are still aspiring towards.